Software is not depreciated but amortized, as it is an intangible asset. As per companies act the useful life of software is 3 years. The treatment of depreciation is the same as computers. Following are the software depreciation rates as per the companies act: As of 2021 Nature of Asset Useful LifeRead more
Software is not depreciated but amortized, as it is an intangible asset. As per companies act the useful life of software is 3 years. The treatment of depreciation is the same as computers. Following are the software depreciation rates as per the companies act:
As of 2021
| Nature of Asset | Useful Life | Depreciation | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Servers and networks | 6 years | 39.30% | 15.83% |
| End-user devices such as desktops, laptops, etc. | 3 years | 63.16% | 31.67% |
For example, XYZ Ltd purchased a new accounting software on 1 October for Rs.50,000. As per the Companies Act, the useful life of software is 3 years. Hence, the software will be amortized for 3 years and the company amortizes on the straight-line method.
Amortization amount = 50,000*31.67%
For full year = Rs.15,835
As the software was purchased on 1 October hence it will be amortized for 6 months.
For 6 months = 15,835*6/12
= Rs.7,917.50
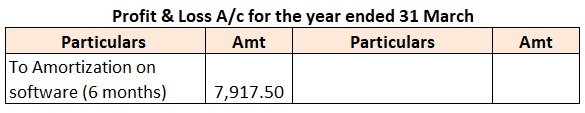
Amortization is the same as depreciation. Hence, treatment will also be the same. The amortization amount will be transferred to the Profit & Loss A/c on the debit side as a non-cash expense.
See less

Debtors and Creditors Points of Distinction Debtors Creditors Meaning A debtor is a person or entity that owes money to the other party (the other party is also known as the creditor). A creditor is a person or entity to whom money is owed or who lends money. Nature The debtors will have a debit balRead more
Debtors and Creditors
Example:
Mr. A purchases raw materials from its supplier Mr. D on credit.
Here for Mr. D, Mr. A will be a debtor because the amount is receivable from him.
Similarly, for Mr. A, Mr. D will be his creditor because the amount is payable to him.
Profit and Gain
Profit = Total Income-Total Expenses
Net profit
Operating profit
Capital gain
Long term capital gain
Short term capital gain
Example: A company’s sales for the period are $60,000 and expenses incurred are $40,000. Here the profit calculated will be $20,000 because revenue exceeds expenses.
Profit = Total Income-Total Expenses
= 60,000 – 40,000
= $20,000
Mr. X owned land worth $10,00,000 and after 10 years he sold it at a current market value of $14,00,000. So the gain he earned is $4,00,000. This gain of $4,00,000 will be termed as a capital gain since land is a capital asset.
See less