Introduction Internal reconstruction refers to the process of restructuring a sick company’s balance sheet by certain methods to turn it financially healthy, thus saving it from potential liquidation. Explanation When a company has been making losses for many years, it has a huge amount of accumulatRead more
Introduction
Internal reconstruction refers to the process of restructuring a sick company’s balance sheet by certain methods to turn it financially healthy, thus saving it from potential liquidation.
Explanation
When a company has been making losses for many years, it has a huge amount of accumulated losses due to which the reserve and surplus appear at a very low or negative amount in the balance sheet.
Also, such a company is said to be overcapitalised as it is not able to generate enough returns to its capital.
As the company is overcapitalised, the assets are also overvalued. The balance sheet also contains many fictitious assets and unrepresented intangible assets.
The balance sheet of such a ‘sick’ company looks like the following:
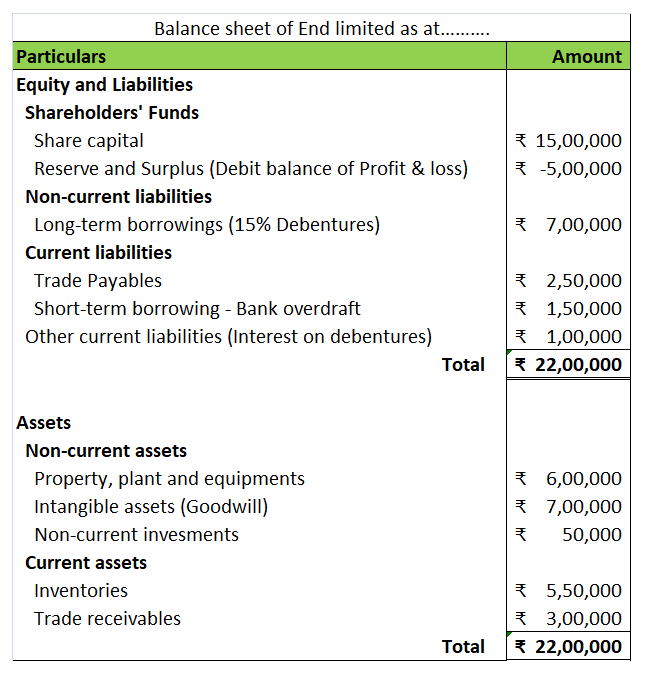
Hence, to save the company from liquidation,
- its assets and liabilities are revalued and reassessed,
- its capital is reduced by paying off part of paid-up capital to shareholders or cancelling the paid-up capital.
- the right of shareholders related to preference dividends is altered,
- agreements are made with creditors to reduce their claims and
- fictitious assets and accumulated losses are written off.
In this way, its balance sheet gets rid of all undesirable elements and the company gets a new life without being liquidated. This process is known as internal reconstruction.
Legal compliance
The internal reconstruction of a company is governed by the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013.
See less


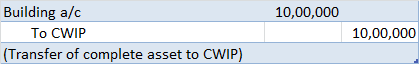
No, Goodwill cannot be called a fictitious asset. A fictitious asset does not have any physical existence or realizable value. Although it is recorded in the assets column, it is not really an asset, rather it is an expense that is incurred during the accounting period. Its benefit, however, is realRead more
No, Goodwill cannot be called a fictitious asset.
A fictitious asset does not have any physical existence or realizable value. Although it is recorded in the assets column, it is not really an asset, rather it is an expense that is incurred during the accounting period. Its benefit, however, is realized for extended periods. This is why they are recorded as assets. They are recorded in a single year and are amortized over the years. A fictitious asset is neither tangible nor intangible.
Examples of Fictitious Assets
Now, goodwill is an intangible asset that relates to the purchase of a company. It is the amount that a company pays over the net worth of the company being purchased. This can be because of its brand value, good customer base, etc. As a company’s reputation improves, its goodwill increases accordingly. Therefore, It does not have a tangible existence but it does have a monetary value. They are also recorded on the asset side of the balance sheet under the head “Intangible assets”.
Reason for not being a fictitious asset
Since goodwill is an asset and not an expense, it cannot be called a fictitious asset. Moreover, goodwill has a realizable value. Unlike fictitious assets, goodwill can be purchased or sold. Therefore, goodwill is termed as an intangible asset but not a fictitious asset. The major difference between an intangible asset and a fictitious asset is:

See less