Interest on Investment is to be shown on the Credit side of a Trial Balance. Interest on investment refers to the income received on investment in securities. These securities can be shares, debentures etc. of another company. When one invests in securities, they are expected to receive a return onRead more
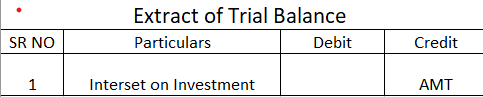
Interest on Investment is to be shown on the Credit side of a Trial Balance.
Interest on investment refers to the income received on investment in securities. These securities can be shares, debentures etc. of another company. When one invests in securities, they are expected to receive a return on investment (ROI).
Since interest on investment is an income, it is shown on the credit side of the Trial Balance. This is based on the accounting rule that all increase in incomes are credited and all increase in expenses are debited. A Trial Balance is a worksheet where the balances of all assets, expenses and drawings are shown on the debit side while the balances of all liabilities, incomes and capital are shown on the credit side.
For example, if Jack bought Corporate Bonds of Amazon, worth $50,000 with a 10% interest on investment, then the accounting treatment for interest on investment would be
Cash/Bank A/C Dr 5,000
To Interest on Investment in Corporate Bonds (Amazon) 5,000
As per the above entry, since interest on investment is credited, it will show a credit balance and hence be shown on the credit side of the Trial Balance. Interest on investment account is not to be confused with an Investment account. Investment is an asset whereas interest on investment is an income.
See less


Fictitious assets On seeing or hearing ‘fictitious’, the words which come to our mind are ‘not true, ‘fake’ or ‘fantasy’. So, fictitious assets are those items that appear on the assets side of the balance sheet but are actually not assets. In substance, fictitious assets are the expenses and lossesRead more
Fictitious assets
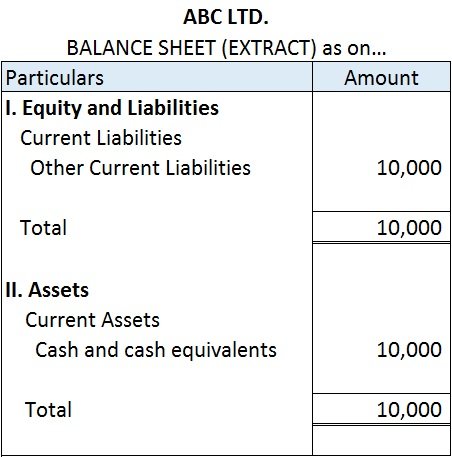
On seeing or hearing ‘fictitious’, the words which come to our mind are ‘not true, ‘fake’ or ‘fantasy’. So, fictitious assets are those items that appear on the assets side of the balance sheet but are actually not assets.
In substance, fictitious assets are the expenses and losses that are not completely written off in a financial year and are required to be carried forward to the next financial year.
The examples of fictitious assets are as follows:
Fictitious assets appear on the asset side of the balance sheet as expenses and losses have a debit balance.
*when the balance sheet is prepared as per Schedule III of Companies Act, the Net loss is shown as a negative figure under the head Reserve and Surplus.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets mean the assets which don’t have any physical existence. They cannot be seen or touched but are assets because they do provide future economic benefits to the business. Like tangible assets (like machinery and building), they can be also created, purchased or sold.
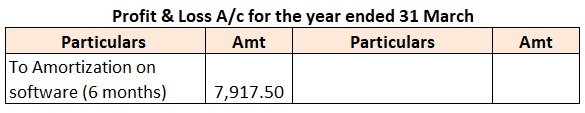
Like tangible assets are depreciated, intangible assets are gradually written over by amortization over their useful lifespan to account for the economic benefits provided by them.
Following are the examples of intangible assets:
Intangible assets which are created by the business-like goodwill or brand recognition do not appear in the balance sheet.
Only acquired intangible assets can be shown in the balance sheet. Like purchased goodwill, patents, trademarks etc.
Intangible assets also face impairment if their fair value is less than their carrying value after deducting amortization expense. The difference between carrying value and fair value is shown in the Profit and loss A/c as impairment charge and the asset is valued at fair value in the balance sheet.
See less