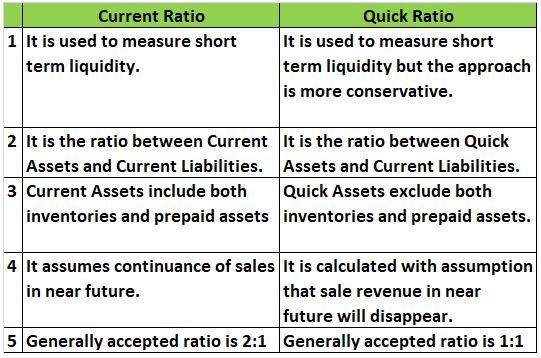
The current ratio is a liquidity ratio that measures a firm’s ability to pay off its short-term liabilities with its current assets. The current ratio is important because short-term liabilities are due within a period of twelve months. The current ratio is calculated using two standard figures thatRead more
The current ratio is a liquidity ratio that measures a firm’s ability to pay off its short-term liabilities with its current assets. The current ratio is important because short-term liabilities are due within a period of twelve months.
The current ratio is calculated using two standard figures that are shown in the company’s balance sheet: current assets and current liabilities. The formula for the same goes as:
Current ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
A current ratio of 2:1 is considered ideal. Generally, a ratio between 1.5 to 2 is considered beneficial for the business, which means that the company has more financial resources (Current Assets) to cover its short-term debt (Current Liabilities).
A high current ratio may indicate that the business is having difficulties managing its capital efficiently to generate profits.
On the other hand, a lower current ratio (especially lower than 1) would signify that the company’s current liabilities exceed its current assets and the business may have difficulty covering its short-term debt. Although the definition of a good current ratio may vary in the different industry groups.
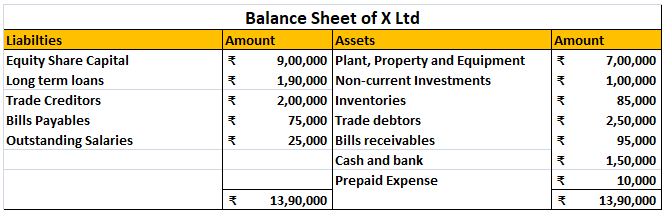
Example- Where,
1) CR is 2:1, the company is in a good situation as it has double the Current Assets in order to cover the short-term debt.
2) CR is 0.5:1, the company is not in a good situation as it has only half the Current Assets in order to cover the short-term debt.
See less

Profitability ratios measure how profitable a company is and are used to assess its performance and efficiency. Based on the income statement and balance sheet of a company, these ratios are calculated. In terms of profitability ratios, there are several types, each providing a different viewpoint.Read more
Profitability ratios measure how profitable a company is and are used to assess its performance and efficiency. Based on the income statement and balance sheet of a company, these ratios are calculated.
In terms of profitability ratios, there are several types, each providing a different viewpoint.
The following are some common profitability ratios:
Gross profit margin: This ratio measures the percentage of revenue that remains after the cost of goods sold has been deducted. Producing and selling efficiently is indicated by this metric.
Net profit margin: An organization’s net profit margin is the portion of revenue left after all expenses have been deducted. A company’s profitability is measured by this indicator.
Return on assets (ROA): This ratio measures how profitable a company’s assets are. In other words, it indicates how effectively a company generates profits from its assets.
Return on equity (ROE): This ratio measures the profitability of a company’s equity. It shows how effectively a company generates profits from its shareholders’ investments.
Analysts and investors use profitability ratios to evaluate a company’s performance and profitability ability.
An investor or analyst can evaluate a company’s relative strength and identify potential opportunities or risks by comparing its profitability ratios with its peers or its industry averages.
See less