Errors revealed by Trial Balance Trial balance, as we know, is a statement prepared after the ledger, followed by a journal. It has a list of all the general ledger accounts contained in the ledger of a business. Each nominal ledger account either holds a debit balance or credit. It is primarily useRead more
Errors revealed by Trial Balance
Trial balance, as we know, is a statement prepared after the ledger, followed by a journal. It has a list of all the general ledger accounts contained in the ledger of a business. Each nominal ledger account either holds a debit balance or credit.
It is primarily used to identify the balance of debits and credits entries from the transactions recorded in the general ledger in a certain accounting period. The debit and credit sides total are equal in a trial balance.
Classification of errors in the trial balance
- Errors of Commission: Errors arising due to wrong posting of a journal entry, a ledger account, wrong totaling of a subsidiary book, or even wrong recording of accounts. Therefore, resulting in trial balance error. E.g business receives an amount on goods sold on credit but it is instead posted to additional capital a/c.
- Errors of Omission: This occurs when some transactions are fully or partially omitted from books of accounts. A complete omission is a case when the transaction is completely omitted but a partial omission is seen when the transaction is entered in the journal but not posted to the ledger. E.g a cheque worth $4,100 was received from ABC Ltd. but completely omitted. Then the rectification entry shall be passed later on.
- Compensating Errors: It occurs when the errors are equal in amount and opposite to each other so and so that they cancel each other which further creates no difference in the Trial Balance. E.g Harry’s account is debited to $300 wrongly instead of $400. On the other hand, Liam’s account is credited by $700 instead of $800.
- Errors of Principles: These are the errors occurring when the entries that are posted are incorrect, violating the accounting policy. E.g when receiving money from debtor then debiting debtor and crediting the amount of money received.
Some of the common errors
Some more (commonly seen) errors while preparation of the trial balance:
Errors of Commission
- Addition or totaling mistakes in the trial balance, debit, and credit side.
- Wrong totaling of subsidiary books.
- Error in the sum total of subsidiary book.
- Posting in the wrong account.
- Recording a transaction incorrectly in a journal.
- Balance wrote on the wrong side of the trial balance.
- Error in posting a journal to a ledger.
- Posting on the wrong side of the account.
Errors of Omission
- Goods purchased and returned to the supplier may be entered in the purchase returns book but not posted in the debit of the supplier account.
- Cash paid to creditors was completely omitted from the recording.
Compensating Errors
- Wrong posting of the same amount in another account, which may not be affecting the equalizing of trial balance.
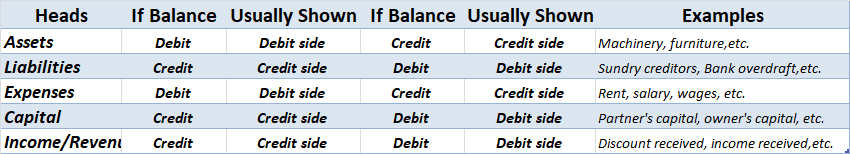
Errors of Principles
- Posting twice to a ledger account.
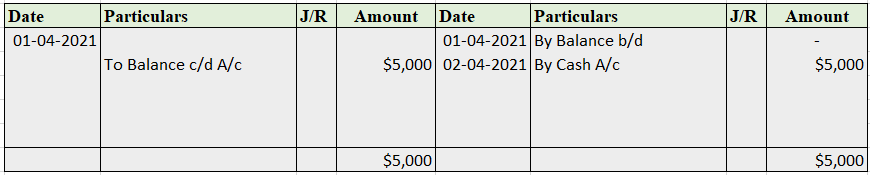
- Balance c/d or balance b/d is written on the wrong side of the ledger account.
- Reversal of a journal entry by mistake like, crediting cash and debiting debtor’s a/c.
See less

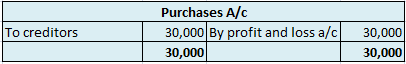
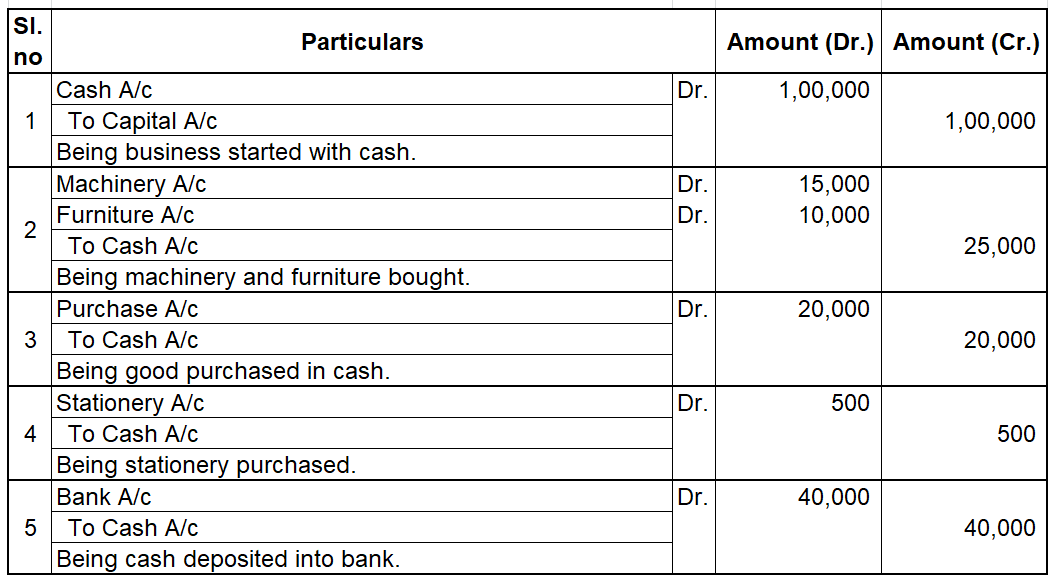
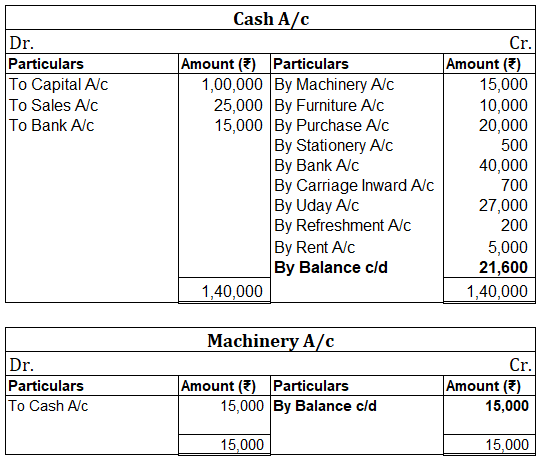
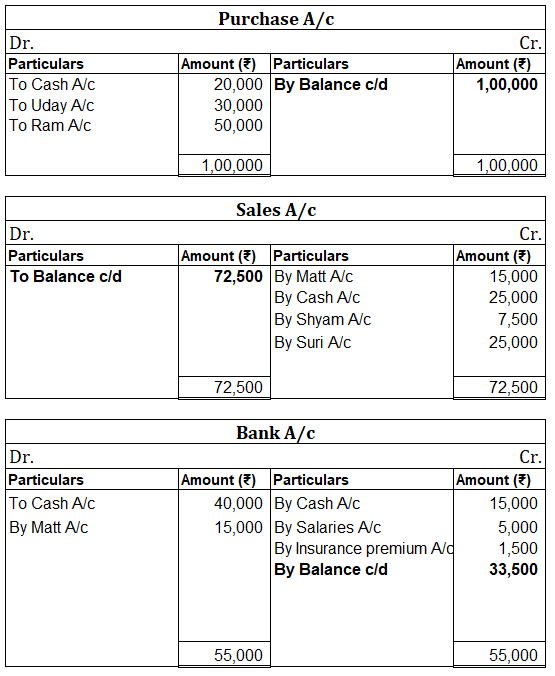
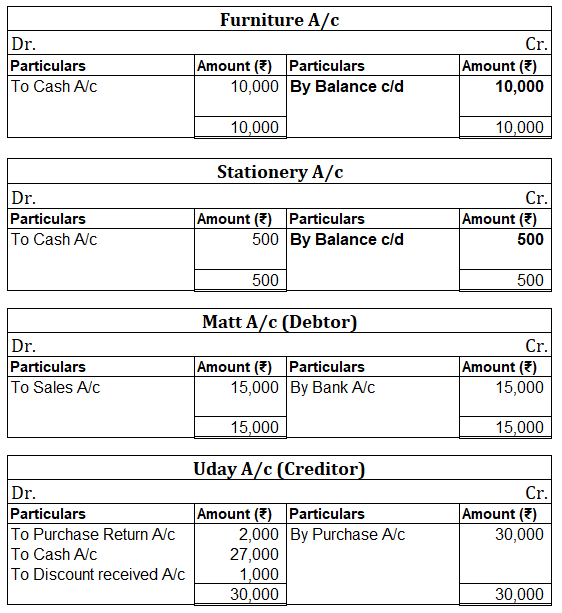
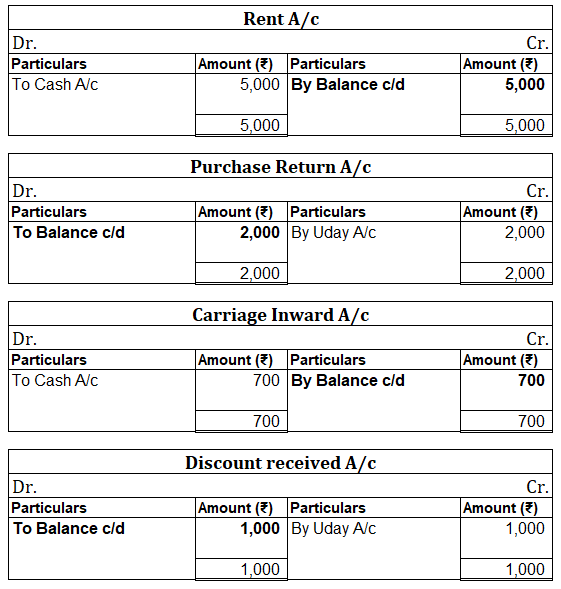
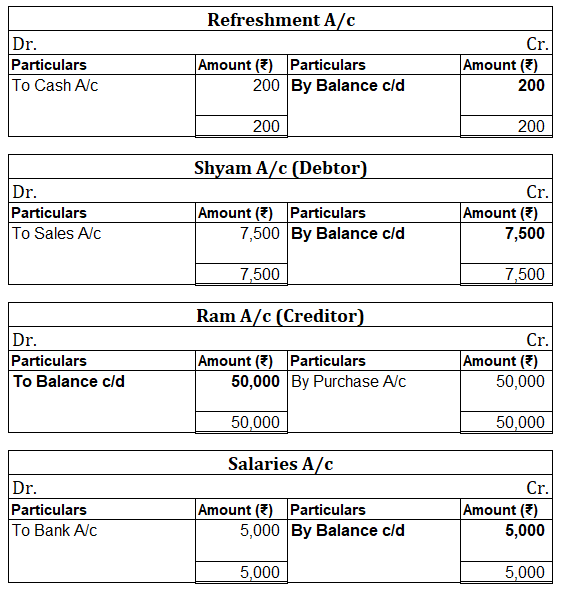
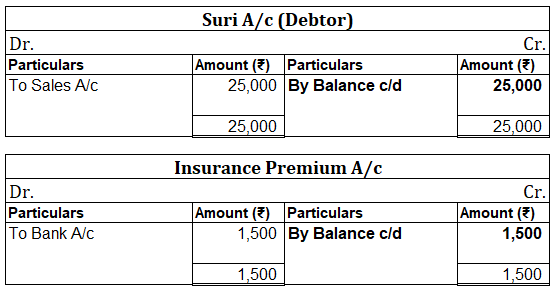
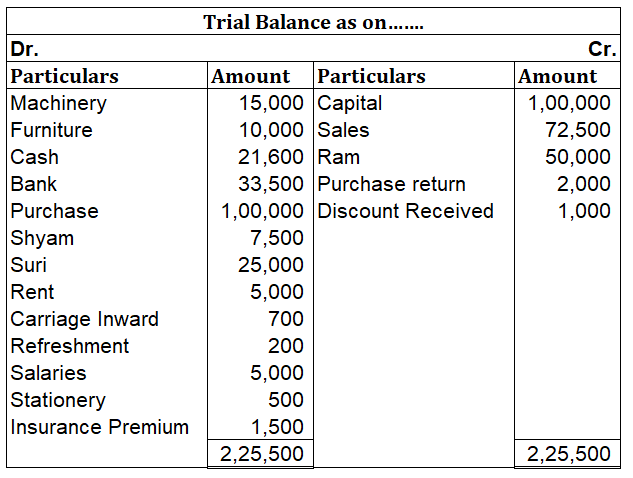
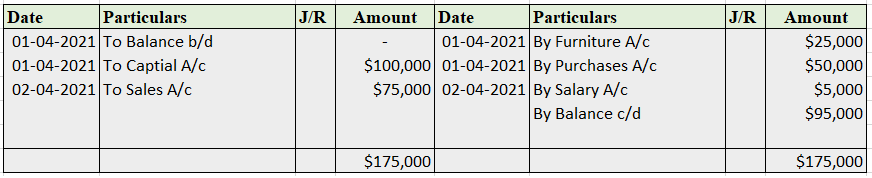


When in a single transaction two or more accounts are involved, such kinds of transactions are termed as Compound entries. Example 1, Johnson Co. purchased goods worth 5,000, and half of the amount was paid in cash and the other half by cheque. So here three accounts are involved: Purchase account-Read more
When in a single transaction two or more accounts are involved, such kinds of transactions are termed as Compound entries.
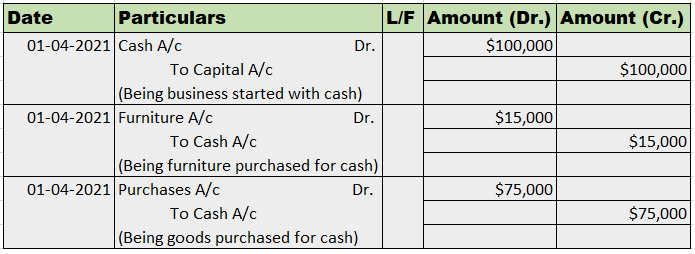
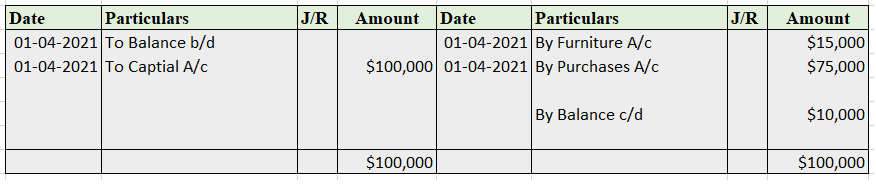
Example 1, Johnson Co. purchased goods worth 5,000, and half of the amount was paid in cash and the other half by cheque.
So here three accounts are involved:
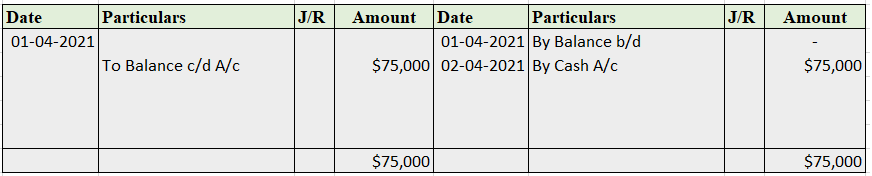
Purchase account- That is to be debited.
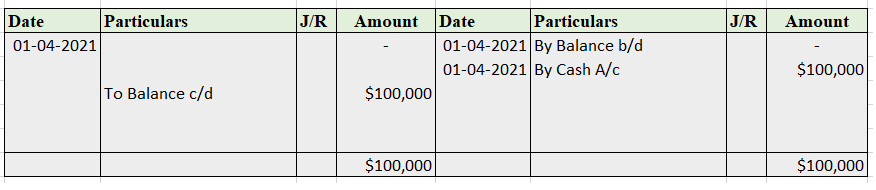
Cash account- That is to be credited.
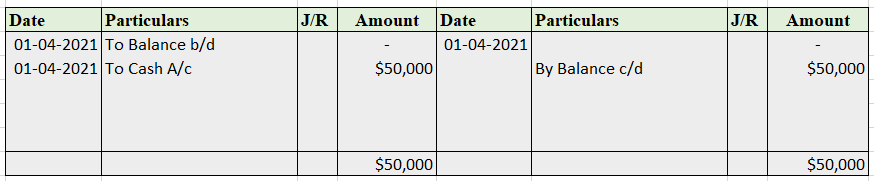
Bank account- That is to be credited.
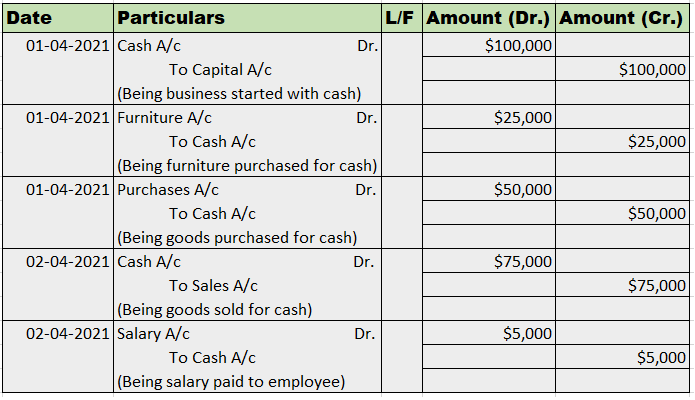
Journal entry:
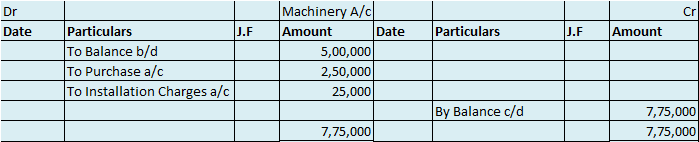
Now posting the above journal entry in a ledger account.
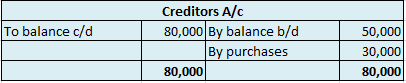
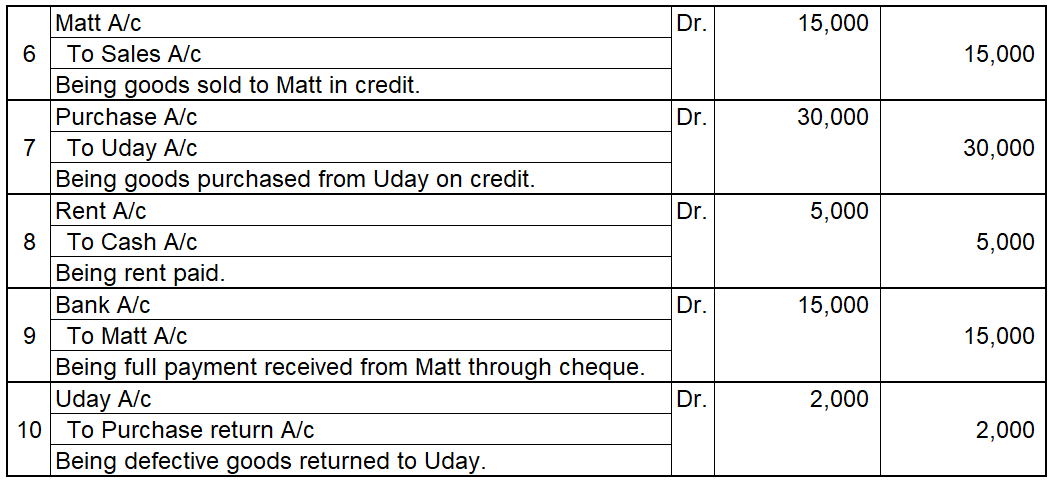
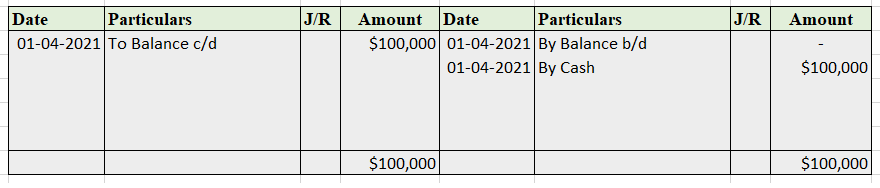
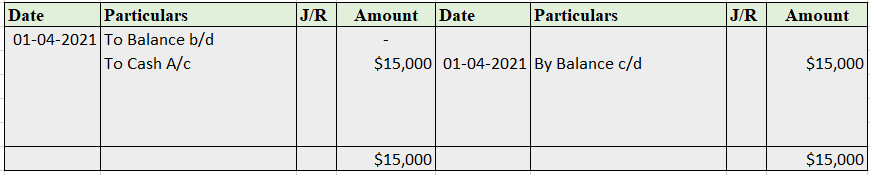
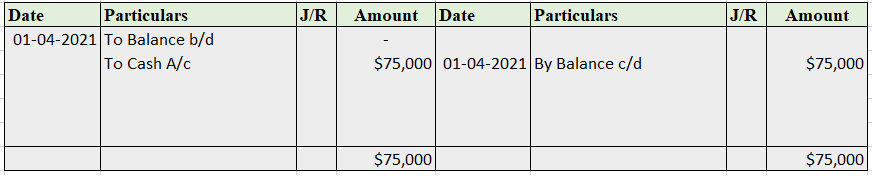
In the Journal, the Purchase account has been debited. So in the ledger, the purchase account will also be debited. Since the purchase account is debited in the ledger, the corresponding two credit accounts of this entry i.e. the cash and the bank will be written on the debit side in the particulars column. So while posting, the amount to be considered would be the amount individually paid in cash and bank as shown in the journal entry.
Cash a/c is credited with the purchase account. In the ledger, purchase a/c will be posted on the credit side. So while posting, the amount to be considered would be the amount individually paid in cash.
Bank a/c is credited with the purchase account. In the ledger, purchase a/c will be posted on the credit side. So while posting, the amount to be considered would be the amount individually paid in Bank a/c.
Example 2, Johnson Co purchased goods and made payment in cash 2,000. Along with it, it also paid commission and interest of 1,000 and 500 respectively.
So here four accounts are involved:
Purchase account- That is to be debited.
The commission allowed account- That is to be debited.
Interest allowed account- That is to be debited.
Cash account- That is to be credited.
Journal Entry:
Now posting the above journal entry in a ledger account.
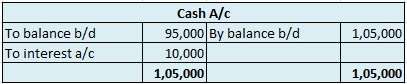
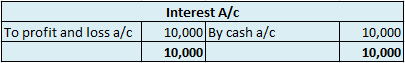
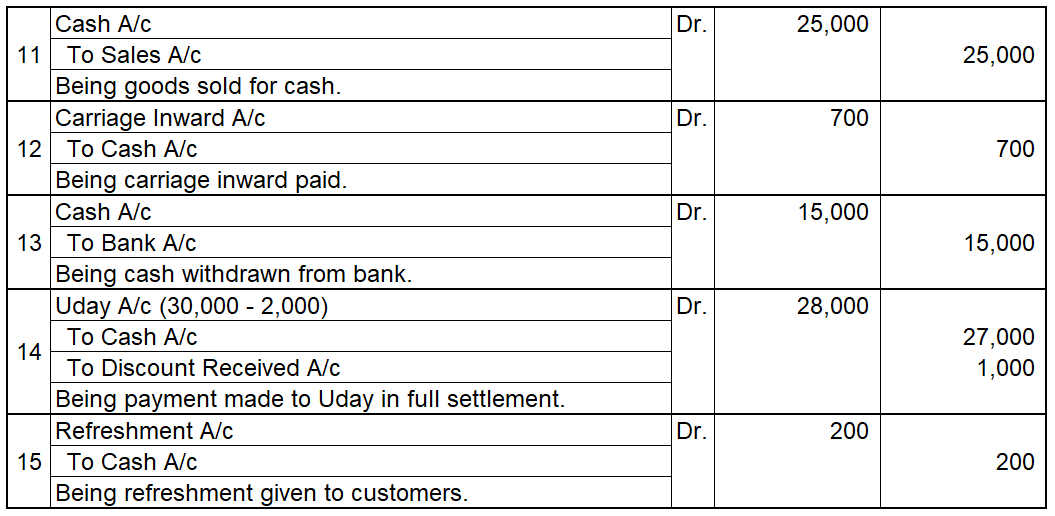
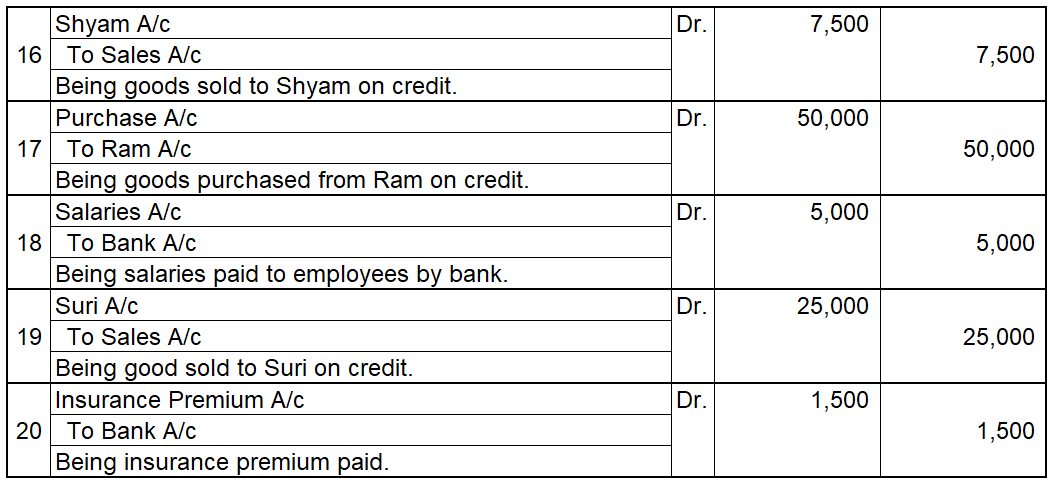
In the journal entry, the cash account has been credited. So in the ledger, the cash account will also be credited. Since the cash account is credited in the ledger, the corresponding three accounts will also be credited in the particulars column. As in the journal entry the three debit accounts viz. Purchase, the commission allowed, and interest allowed, the amounts written against them shall be entered in the respective accounts in the amount column on the credit side of the cash account.
Purchase a/c is debited with a cash account. In the ledger, Cash a/c will be posted on the debit side. So while posting, the amount to be considered would be the amount individually paid in the Purchase account.
The commission allowed a/c is debited with a cash account. In the ledger, cash a/c will be posted on the debit side. So while posting, the amount to be considered would be the amount individually paid in Commission allowed a/c.
Interest allowed a/c is debited with a cash account. In the ledger, cash a/c will be posted on the debit side. So while posting, the amount to be considered would be the amount individually paid in Interest allowed a/c.
See less