There are two types of ledger accounts in the accounting system – temporary and permanent. Temporary accounts are those whose balances zero out and we do not carry forward balances to the next year. Examples are revenue and expenses accounts or nominal accounts. The balances of such accounts are traRead more
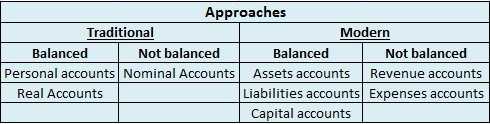
There are two types of ledger accounts in the accounting system – temporary and permanent.
Temporary accounts are those whose balances zero out and we do not carry forward balances to the next year. Examples are revenue and expenses accounts or nominal accounts. The balances of such accounts are transferred to the profit and loss account and therefore are not balanced.
Permanent accounts are those whose balances are carried forward to the next accounting year in form of opening balances. These accounts are balanced and such balances are transferred to the balance sheet. Examples are assets, liability and capital accounts or personal and real accounts.
Balancing an account means equaling both the debit and the credit side of the account. Generally, there is a difference between the accounts recorded as a carry down balance in the case of permanent accounts and as a transfer balance in the case of temporary accounts.
Balancing serves as a check to the double-entry rule of accounting.
Balanced accounts
As discussed above, the balanced accounts are shown in the balance sheet and the balancing figure for such accounts are carried forward to the next accounting period.
Unbalanced accounts
As per the above discussion, the balancing figures of unbalanced accounts are transferred to the profit and loss account and no balances are carried forward to the next accounting period.
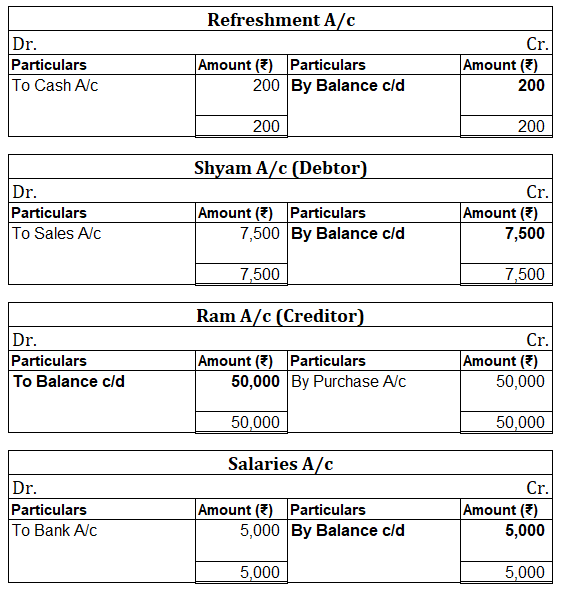
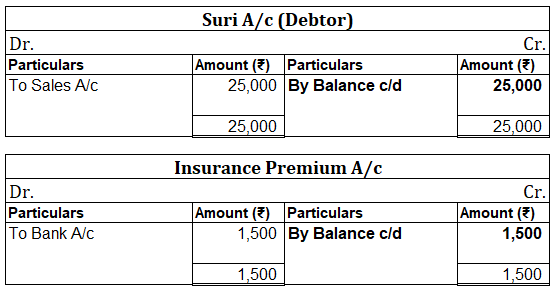
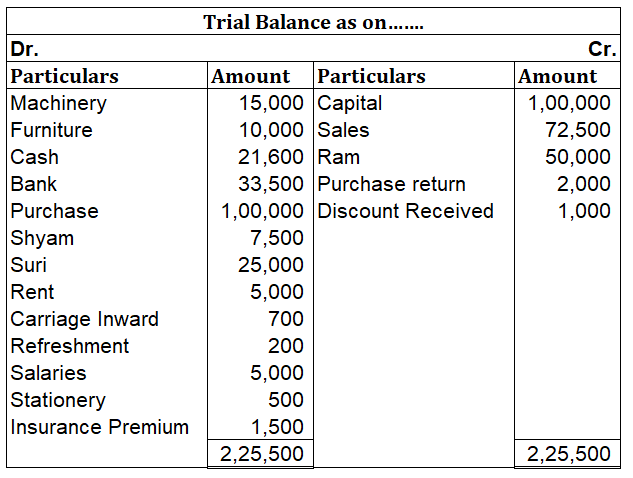
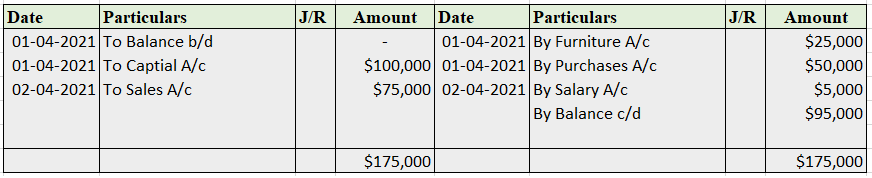
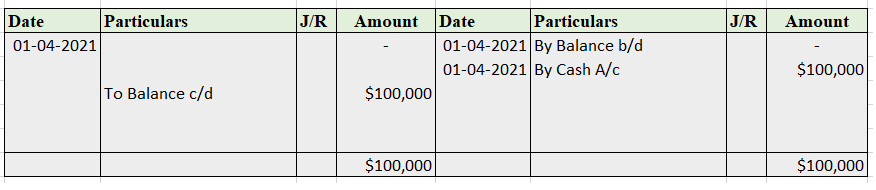
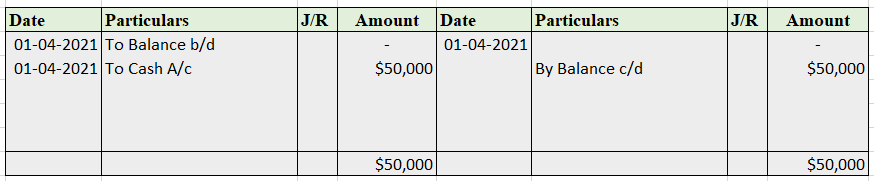
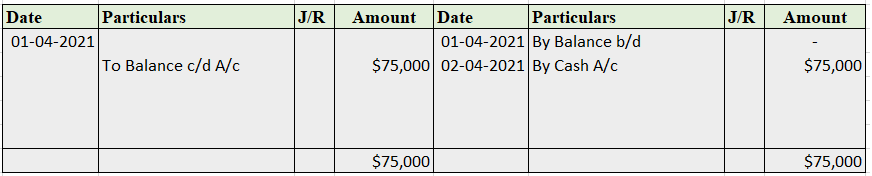
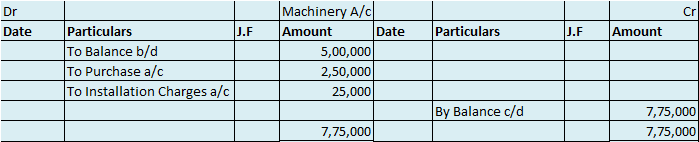
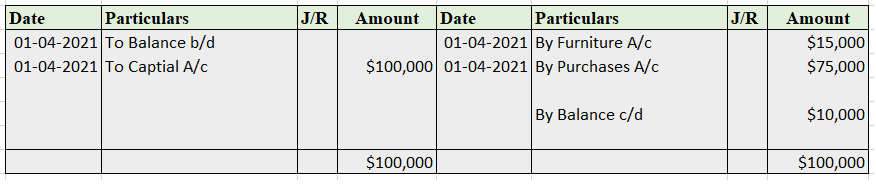
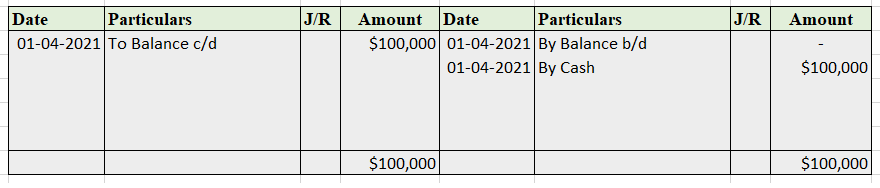
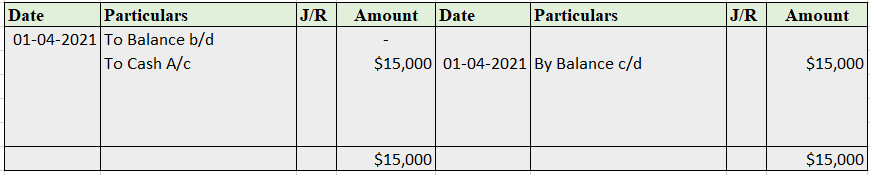
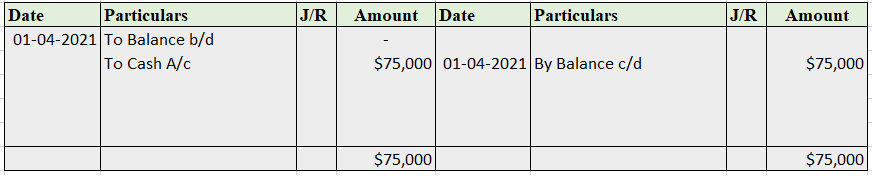
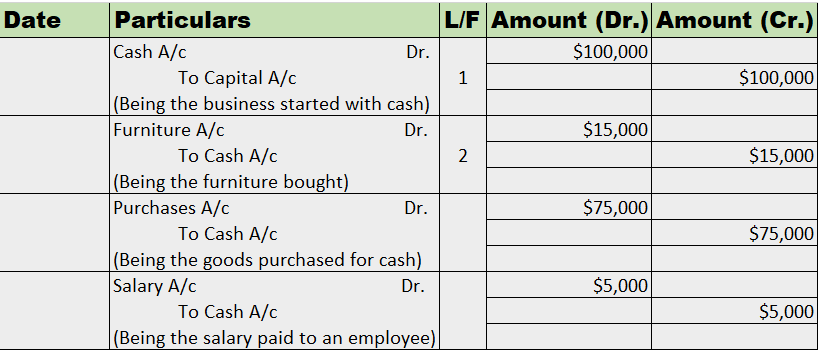
Suppose a company Shine Ltd. has machinery costing 5,00,000 at the beginning of the accounting period and charges depreciation of 10% on the asset. The company also has creditors amounting to 50,000 at the beginning of the period and purchases goods amounting to 30,000 on credit. It has a cash balance of 95,000 at the beginning of the period and earns interest amounting to 10,000.
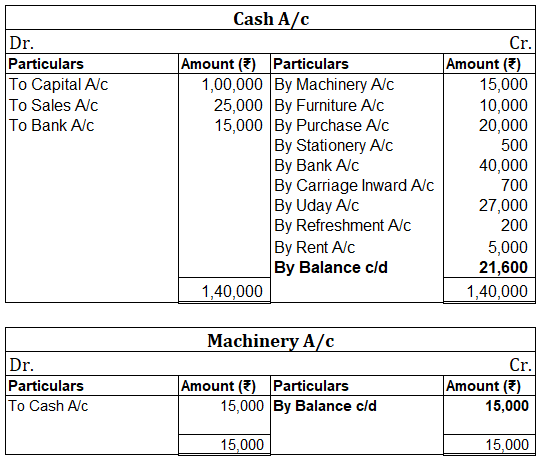
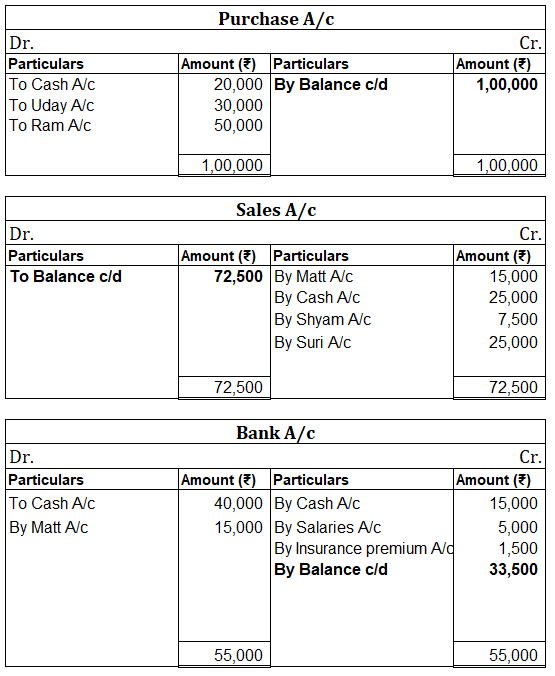
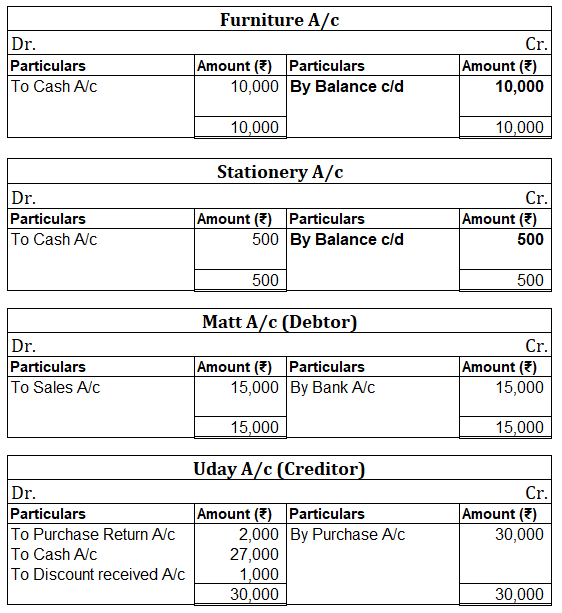
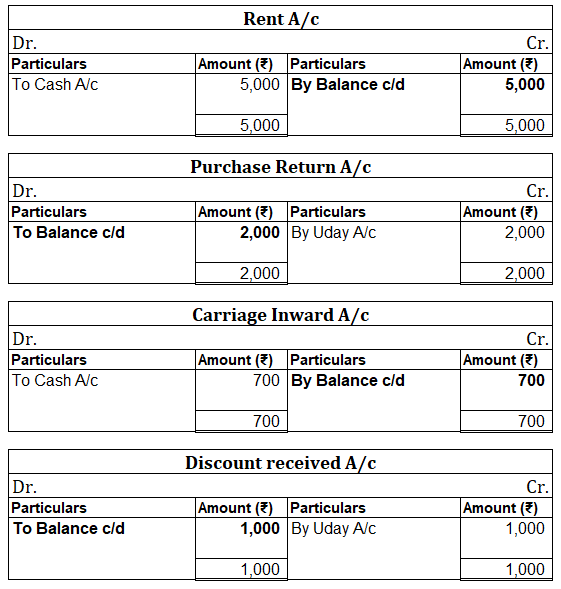
Following ledgers would be prepared to record the above entries:
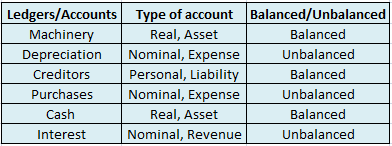
The above ledgers can be shown as follows:
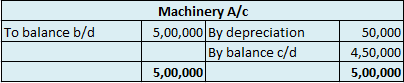
The balance of the machinery account will be shown in the balance sheet and therefore it is a balanced account.
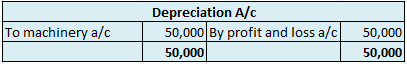
The balance is transferred to the profit and loss account and therefore depreciation account is an unbalanced account.
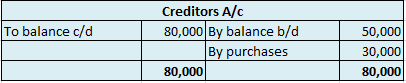
The balance of creditors account will be shown in the balance sheet and therefore it is a balanced account.
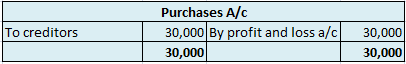
The balance is transferred to the profit and loss account and therefore purchases account is an unbalanced account.
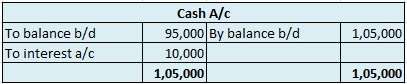
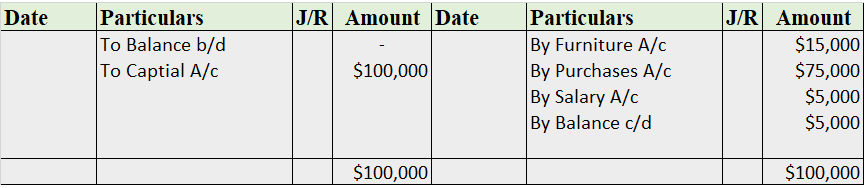
The balance of the cash account will be shown in the balance sheet and therefore it is a balanced account.
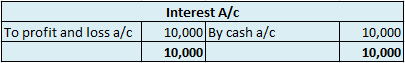
The balance is transferred to the profit and loss account and therefore interest account is an unbalanced account.
See less
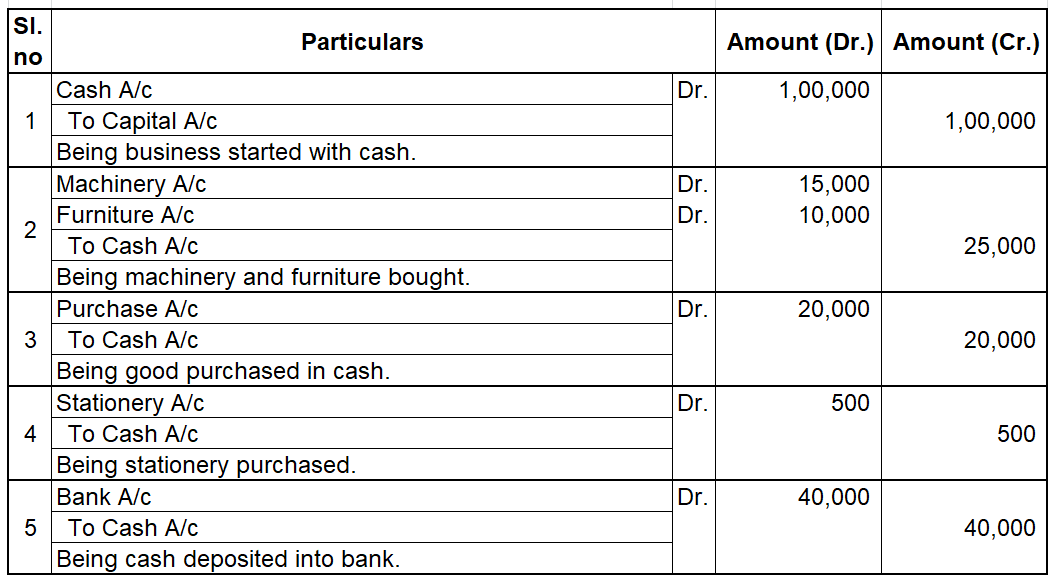
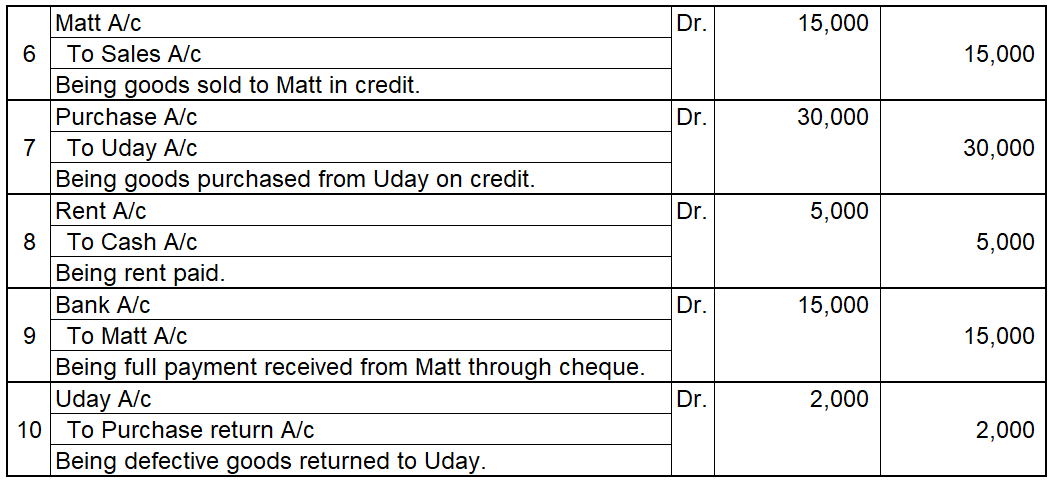
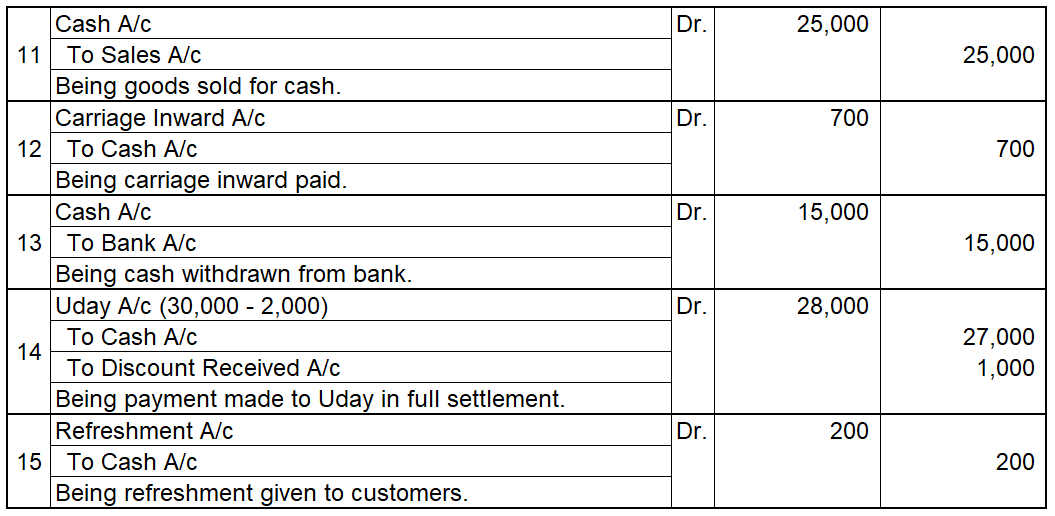
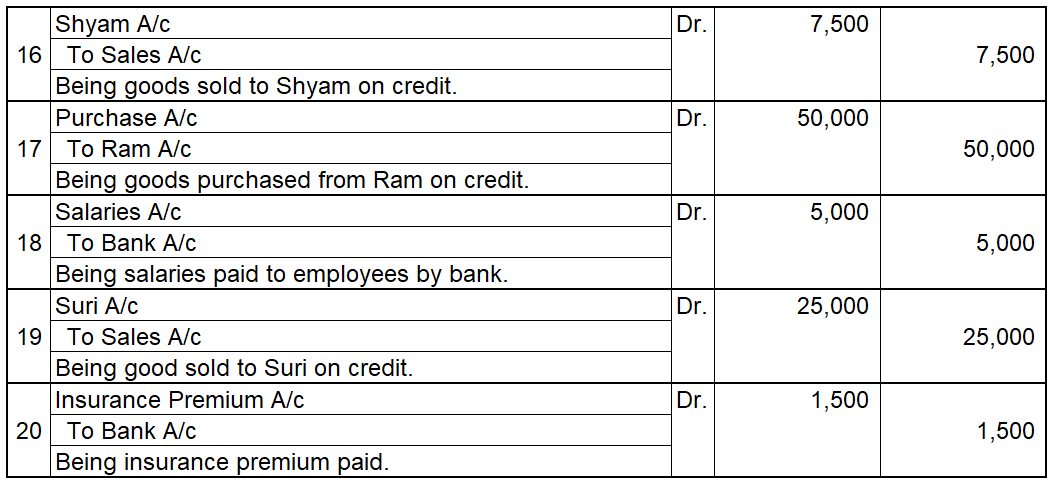
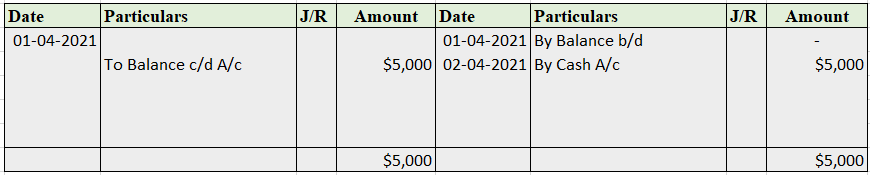

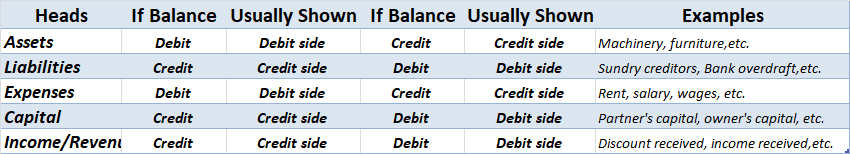

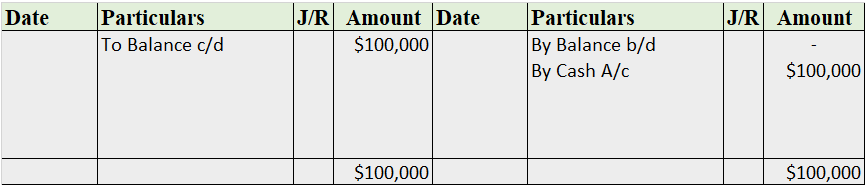
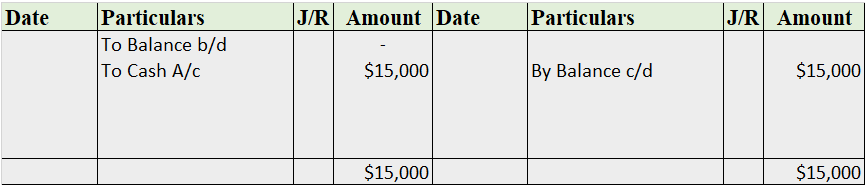
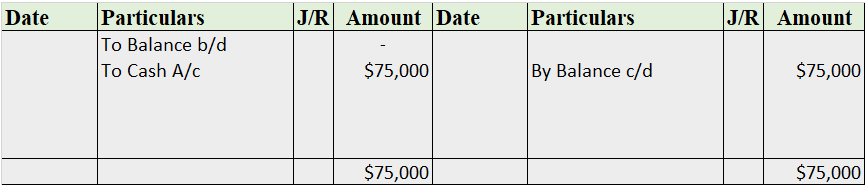
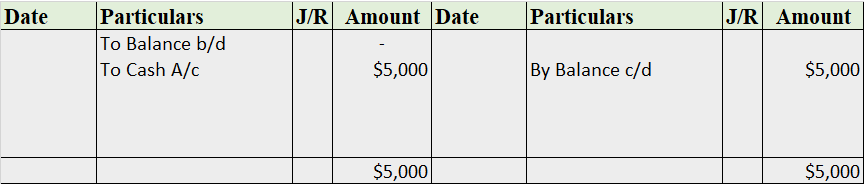
Credit balance means excess of credit side over debit side. For example, At the beginning of the year, the credit balance of trade payable is 3,000 and there is a debit of trade payable of 1,000 during the year and an increase(credit) of trade payable of 4,000 then at the end there will be a creditRead more
Credit balance means excess of credit side over debit side.
For example, At the beginning of the year, the credit balance of trade payable is 3,000 and there is a debit of trade payable of 1,000 during the year and an increase(credit) of trade payable of 4,000 then at the end there will be a credit balance of 6,000 of trade payable at the end
.A Credit balance signifies all income and gains and all liabilities and capital that is there in business.
Liabilities and Capital
Income and Gains
So after seeing all the above points we can conclude that the credit balance includes all the income in the P&L account and all the liabilities in the Balance sheet. So its balance increases when there is an increase in its account.
Debit Balance
Debit balance means excess of credit side over debit side.
For Example- At begining of the year the debit balance of trade receivables is 3,000 and there is a decrease(credit) of trade receivables of 1,000 during the year and an increase(debit) of trade receivables of 4,000 then at the end there will be a debit balance of 6,000 of trade receivables at the end
A Debit balance basically signifies all expenses and losses and all positive balances of assets. The debit balance increases when any asset increases and decreases when any asset decreases.
Asset
Expenses and Loses
- Rent
- Depreciation
- General Expenses
- Loss on Sale of asset
- Printing and stationery
- Audit fees
- Outstanding fees
- Salaries and Wages
- Insurance
- Advertising
- Promotional expenses
See less