Similarly, someone asked Are loose tools current assets
Similarly, someone asked Are loose tools current assets
See lessPlease briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.
Similarly, someone asked Are loose tools current assets
Similarly, someone asked Are loose tools current assets
See lessA revenue reserve is a type of reserve where a portion of the net profit is set aside for future requirements. It serves as a great source of internal finance for the company to meet its short term requirements. The funds put into this reserve are earned from the daily operations of a company. RevenRead more
A revenue reserve is a type of reserve where a portion of the net profit is set aside for future requirements. It serves as a great source of internal finance for the company to meet its short term requirements. The funds put into this reserve are earned from the daily operations of a company. Revenue reserves are shown on the liabilities side of a balance sheet under reserves and surplus. Some examples of revenue reserve are :
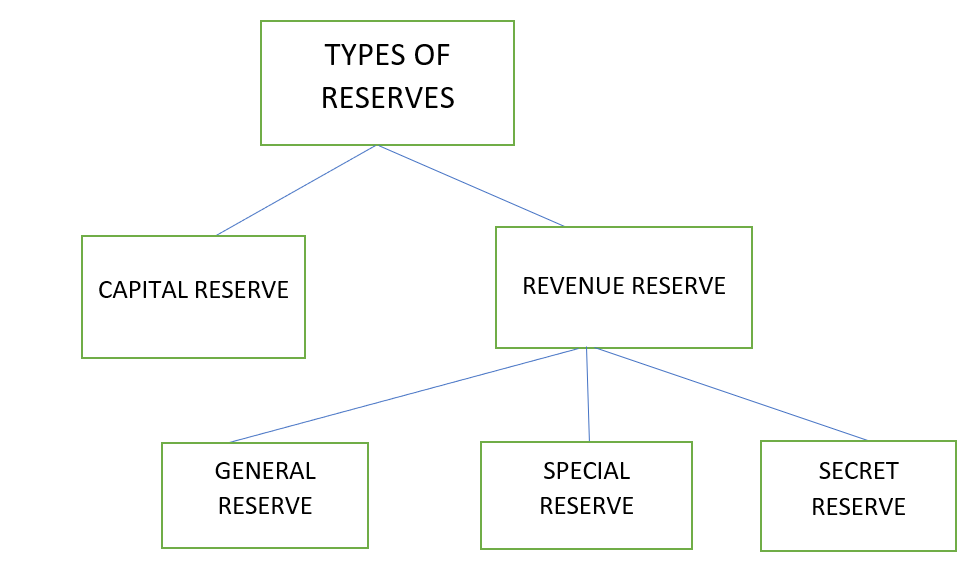
Retained Earnings is that part of the net profit which is left after the distribution of dividends to shareholders. This amount can be invested in the company to gain profits. It is not technically a reserve as it is held after distribution of dividends but it can still be used as one.
On the other hand, a capital reserve is not a part of the revenue reserve. It is created from capital profits to finance long term projects of a company. It is used for specific purposes only.
See lessCapital Accounts record transactions of owners of a business and typically includes amount invested, retained, and withdrawn from the business. In the case of a partnership firm, there are multiple capital accounts as multiple people own the business. Capital Accounts in a partnership firm can be ofRead more
Capital Accounts record transactions of owners of a business and typically includes amount invested, retained, and withdrawn from the business. In the case of a partnership firm, there are multiple capital accounts as multiple people own the business.
Capital Accounts in a partnership firm can be of two types:
A fixed Capital Account is one where only non-recurring transactions related to capital accounts are recorded. For example:
For transactions that are recurring in nature like interest on capital, the interest of drawings a separate account called Partner’s Current Account is created.
Fluctuating Capital Accounts are the ones where there is a single account to record all types of transactions related to the partner’s capital account, whether recurring or nonrecurring.
Fixed Capital Accounts are usually created in cases where there are numerous recurring transactions and partners want to keep a record of the fixed amount invested in the business by all the partners at any point in time.
Fluctuating Capital Account is usually created in cases where the number of recurring transactions is not high or partners want to keep a record of the amount due to all the partners in business at any point in time.
However, the decision to choose what kind of capital account should be implemented in the firm is complete with the partners. They may choose whatever they think is a more suitable fit.
To summarise the difference between the two following table can be used:
| Fixed Capital Account | Fluctuating Capital Account |
| Non-recurring transactions are recorded. | Recurring transactions are recorded. |
| Created where the number of recurring transactions is high to maintain a separate record. | Created where the number of recurring transactions is low. |
| Examples:
· Capital introduced · Capital withdrawn |
Examples:
· Interest on capital · Interest in drawings |
See less
Let us first understand what working capital is. Working capital means the funds available for the day-to-day operations of an enterprise. It is a measure of a company’s liquidity and short term financial health. They are cash or mere cash resources of a business concern. It also represents the exceRead more
Let us first understand what working capital is.
Working capital means the funds available for the day-to-day operations of an enterprise. It is a measure of a company’s liquidity and short term financial health. They are cash or mere cash resources of a business concern.
It also represents the excess of current assets, such as cash, accounts receivable and inventories, over current liabilities, such as accounts payable and bank overdraft.

Any transaction that increases the amount of working capital for a company is a source of working capital.
Suppose, Amazon sells its goods for $1,000 when the cost is only $700. Then, the difference of $300 is the source of working capital as the increase in cash is greater than the decrease in inventory.
Sources of working capital can be classified as follows:
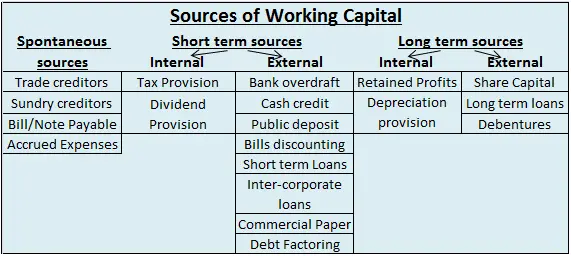
Another point I would like to add is that, although depreciation is recorded in expense and fixed assets accounts and does not affect working capital, it still needs to be accounted for when calculating working capital.
See lessYes, Capital Work in Progress is Tangible Asset. To attain an understanding of the same, we first need to understand what are tangible assets. Assets that have a physical existence, that is they can be seen, touched are called Tangible Assets. Capital work in progress is the cost incurred on fixed aRead more
Yes, Capital Work in Progress is Tangible Asset.
To attain an understanding of the same, we first need to understand what are tangible assets. Assets that have a physical existence, that is they can be seen, touched are called Tangible Assets.
Capital work in progress is the cost incurred on fixed assets that are under construction as on the balance sheet date. Since the asset cannot be used for operation it cannot be classified as a Fixed Asset.
For example:
If an asset takes 1.5 years to be constructed as on 1.4.2020 then on the balance sheet date 31.3.2021, the cost incurred on the asset will be classified as Capital Work in Progress.
Common examples of Capital Work in Progress include immovable assets like Plant and Machinery, Buildings.
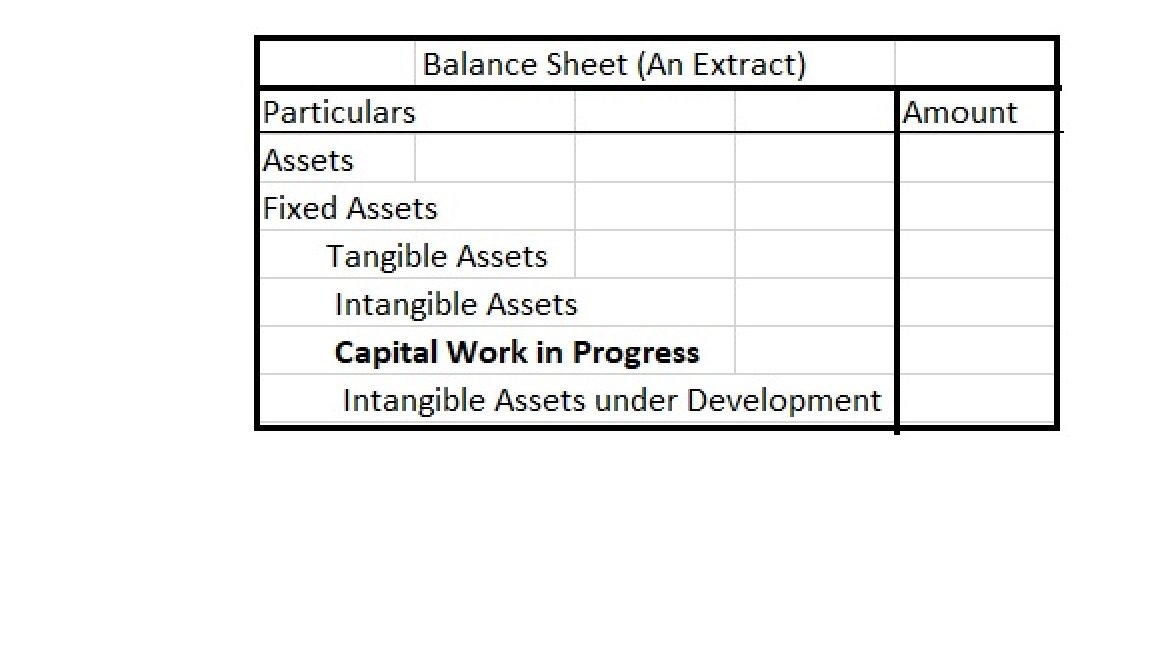
It is shown under the head Non-Current Assets in the balance sheet. Examples of cost included in Capital Work in Progress can be:
Since the assets under the head Capital Work in Progress are in the process of completion and not completed, hence they are not depreciable until completed. Once the asset is completed it is moved under the head Fixed Assets.
Capital Work in Progress is shown in the Balance Sheet as:
Profits earned by a firm are not completely distributed to its owners, some of the profits are retained for various purposes. Reserves are profits that are apportioned or set aside to use in the future for a specific or general purpose. Reserves follow the Conservative Principle of accounting. ReveRead more
Profits earned by a firm are not completely distributed to its owners, some of the profits are retained for various purposes. Reserves are profits that are apportioned or set aside to use in the future for a specific or general purpose. Reserves follow the Conservative Principle of accounting.
Revenue reserve is created from the net profits of a company during a financial year. Revenue reserve is created from revenue profit that a company earns from the daily operations of the business.
Various types of reserves are:
Different parts of profit are apportioned to create a different reserve and those reserves can only be used for purposes as defined.
While accounting for Revenue Reserve, the profit decided to transfer to Revenue Reserve are first transferred to Profit and Loss Appropriation Account and then to Revenue Reserve Account. In the balance sheet, Revenue Account is shown under the Capital and Reserves head.
| Liabilities | Amount | Amount |
| Share Capital | ||
| Reserve and Surplus | ||
| General Reserve | ||
| Capital Redemption Reserve | ||
| Securities Premium Account | ||
| Profit and Loss Account |
Uses of Revenue Reserve:
Example:
Given that Revenue Reserve Account stands at Rs 1,00,000 and the company wants to distribute Rs. 40,000 as dividend to its shareholders. The treatment of this transaction in the financial statements will be-
Particulars Amount (Rs.)
Revenue Reserve Account 1,00,000
(less) Dividend distributed (40,000)
The amount shown in Balance Sheet 60,000
See less
Simply explaining the meaning of the useful life of an asset, it is nothing but the number of years the asset would remain in the business for purpose of revenue generation, making it more simple, the amount of time an asset is expected to be functional and fit for use. It is also called economic lRead more
Simply explaining the meaning of the useful life of an asset, it is nothing but the number of years the asset would remain in the business for purpose of revenue generation, making it more simple, the amount of time an asset is expected to be functional and fit for use. It is also called economic life or service life
It is a useful concept in accounting as it is used to work out depreciation. By knowing this useful life of an asset an entity can easily analyze how to allot the initial cost of an asset across the relevant accounting period rather than doing it unfairly manner.

How do we calculate the useful life of an asset?
The useful life of an asset is not an accounting policy, but an accounting estimate. calculating useful life is not an exact phenomenon but an estimate that is done because it directly impacts how much an asset is to expense every year.
Factors affecting “how long an asset is expected to be useful” depends on some stated points as below:
As per the companies act 2013, some of the useful life of assets are stated below
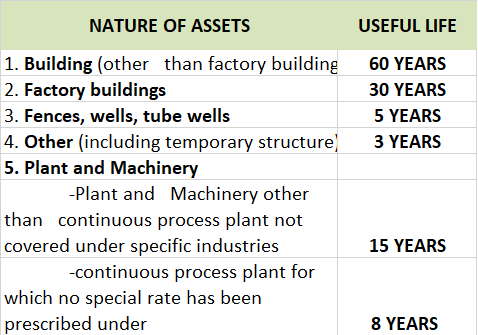
To know more about the different categories of assets you can follow the given link useful life of assets.
POINT TO BE NOTED:- There lies a huge difference in the useful life v/s the physical life of an asset. It is very important to note that amount of time an asset is used in a business is not always be same as an asset’s entire life span.
See less
Capital Redemption Reserve is a statutory reserve, which means it is mandatory for a company to create such reserve when it decides to redeem its preference shares. Capital Redemption Reserve cannot be utilised for any purpose other than the issue of bonus shares. Now let’s understand the reason behRead more
Capital Redemption Reserve is a statutory reserve, which means it is mandatory for a company to create such reserve when it decides to redeem its preference shares. Capital Redemption Reserve cannot be utilised for any purpose other than the issue of bonus shares.
Now let’s understand the reason behind it.
We know preference shares are those shares that carry some preferential rights:
Also, unlike equity shares, preference shares are redeemable i.e. repaid after a period of time (which cannot be more than 20 years).
Generally, the creditors of a company have the right to be repaid first. So, in event of redemption of preference shares, the preference shareholders are repaid before creditors and the total capital of the company will but the total debt of the company is unaffected.
The gap between the debt and equity of the company will further widen and this will also increase the debt-equity ratio of the company. It will be perceived to be a risky scenario by the creditors and lenders of the company because the
So to protect the creditor and lender, Section 55 of the Companies Act comes to rescue.
Section 55 of the Companies Act ensure that the creditors and lenders of a company do not find themselves in a riskier situation when the company decides to redeem its preference shares by making it mandatory for a company to either
OR
OR
This will fill up the void created by the redemption of preference shares and the debt-equity ratio will remain unaffected. Keeping an amount aside in Capital Redemption Reserve ensures that such amount will not be used for dividend distribution and capital will be restored because it can be only used to issue bonus shares.
In this way the debt-equity ratio remains the same, the interest of the creditors and lenders secured.
Bonus shares are fully paid shares that are issued to existing shareholders at no cost.
Let’s take a numerical example for further understanding:
ABC Ltd wants to redeem its 1,000 9% Preference shares at a face value of Rs 100 per share. It has decided to issue 8,000 equity shares @Rs 10 per share and use the profit and reserves to fund the deficit.
The journal entries will be as follows:
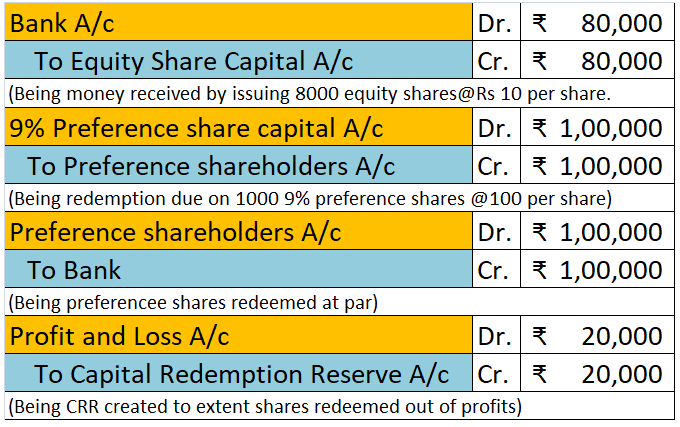
Working note: Rs
9% preference shares due for redemption (1,000 x 10) – 1,00,000
Less: Amount of new shares issued (8,000 x 10) – 80,000
Amount to be transferred to CRR 20,000
Hence, the reduction of total capital by Rs 1,00,000 due to the redemption of preference shares is reversed by issuing equity shares of Rs 80,000 and creating a Capital Redemption Reserve of Rs 20,000.
See less
External liabilities are the amounts which a business is obliged to pay to the outsiders (who are not owners of the business). Here is the list of external liabilities:- Accounts payable ( trade creditors and bills payables) Loan taken from outsiders Loan from bank Debentures Public deposits accepteRead more
External liabilities are the amounts which a business is obliged to pay to the outsiders (who are not owners of the business).
Here is the list of external liabilities:-
The list is not exhaustive.
Just for more understanding, internal liabilities are those liabilities which a business is supposed to pay back to its owners. Such as capital balance, profit surplus etc.
See less
Everyone must have heard about the term “cooking the books”. This term is generally associated with Creative accounting. In simple words, Creative accounting is a method of accounting in which the management tries to show a better picture of the business than the reality. Let us now understand thisRead more
Everyone must have heard about the term “cooking the books”. This term is generally associated with Creative accounting. In simple words, Creative accounting is a method of accounting in which the management tries to show a better picture of the business than the reality. Let us now understand this concept in detail.
What is Creative accounting?
Creative accounting is a method of accounting in which the management manipulates the books of accounts by finding loopholes to showcase a better image of the business.
It is a practice of using accounting loopholes to make a company’s financial position look better than it really is. It is not exactly illegal but it is more of a gray area.
For example, a business may delay reporting expenses to increase the profits to present a better short-term position.
The goal of creative accounting is to impress the shareholders, investors, get loans or boost stock prices.
However, this can also be very risky and have serious consequences. It can reduce the trust of the investors and customers. In some cases, like Enron and WorldCom the world has seen how creative accounting lead to legal consequences.
Common Techniques of Creative Accounting
Some of the common techniques used by the business to manipulate the financial position are as follows:
Ethical implications of Creative Accounting
There are several ethical implications with respect to creative accounting. Some of these are discussed below:
Conclusion
The key takeaways from the above discussion are as follows:
See less