Biological Assets comes under International Accounting Standard IAS 41 Agriculture. IAS 41 Agriculture is the first standard that specifically covers the primary sector. The scope of IAS 41 is accounting for agricultural activity. Agricultural Activity- It is the management of biological transformatRead more
Biological Assets comes under International Accounting Standard IAS 41 Agriculture.
IAS 41 Agriculture is the first standard that specifically covers the primary sector. The scope of IAS 41 is accounting for agricultural activity.
- Agricultural Activity- It is the management of biological transformation by an entity and measuring the change in the quality and quantity of biological assets.
- Biological Transformation- It comprises the process of growth, degeneration, production and procreation that cause qualitative or quantitative changes in a biological asset
- Biological Asset – They are living plants or animals owned by an entity
- Agricultural Produce- It is the harvested / detached product of the entity’s biological asset.
IAS 41 does not apply to
- Agricultural land
- Intangible assets related to agricultural activity
- Products that are the result of processing after the point of harvest, for example, yarn, carpet, rubber, wine, etc
- The land on which the biological assets grow, regenerate, degenerate.
Biological Assets
Definition
Biological assets are living plants or animals that go through biological transformation, owned by an entity to prepare agricultural produce for the purpose of agricultural activities only.
Living plants include plants that are consumable within 1 year and are harvested. It also includes plants that are used for lumbering and wood-cutting activities.
Examples
Examples of biological assets are:
Sheep, pigs, poultry, beef cattle, fish, dairy cows, plants for harvest etc
Importance
- Farming: They are key to agriculture and food production.
- Income: They generate substantial income for businesses in industries such as vineyards, livestock, silviculture, etc.
- Sustainability: Properly managing them helps the environment.
Accounting & Presentation
Recognition
Under IAS 41 biological assets are recognised when
- The business must have ownership over them from a past event.
- The future economic benefits are expected to flow to the business from their ownership.
- The cost or fair value of the asset can be measured reliably.
Agricultural produce is recognised
- It is recognised at the point of harvest or detachment.
Agricultural produce is derecognised when
- They enter the trading.
- Enters the production process.
Measurement
- Biological assets are measured on initial recognition and at each balance sheet date at their fair value less costs to sell.
- Costs to sell are incremental costs incurred in selling the asset.
- Agricultural produce is measured at the point of harvest, at fair value less costs to sell at the point of harvest.
- Agricultural produce after the point of harvest/ detachment is transferred and treated under the IAS 2 Inventory
Gains & Losses
- Gains and losses arising from the initial recognition of biological assets are reported in the statement of profit and loss.
- The change in fair value less costs to sell of a biological asset between balance sheet dates is reported as gain or loss in the statement of profit and loss.
- A gain or loss arising on initial recognition of agricultural produce at fair value less selling costs is included in profit or loss for the period in which it arises.
Treatment
- The sale of agricultural produce is treated as revenue in the statement of profit and loss.
- Agricultural produce to be harvested for more than 12 months, livestock to be held for more than 12 months and trees cultivated for lumber are recorded as Biological assets under the Non-current assets head in the balance sheet.
- Agricultural produce to be harvested within 12 months, livestock to be slaughtered within 12 months and annual crops like wheat, and maize are recorded as Biological assets under the head Current assets in the balance sheet.
- Inventories produced from agricultural produce are presented as Inventory under the head Current assets in the balance sheet.

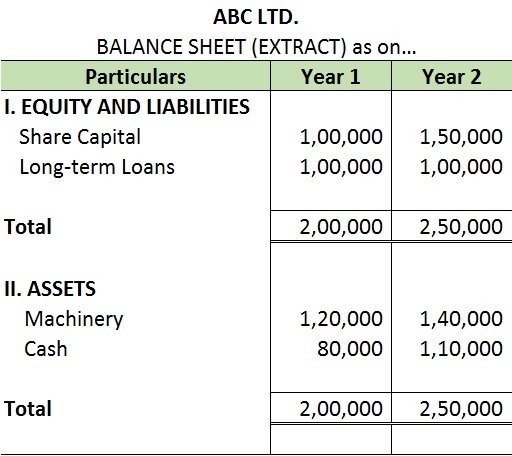
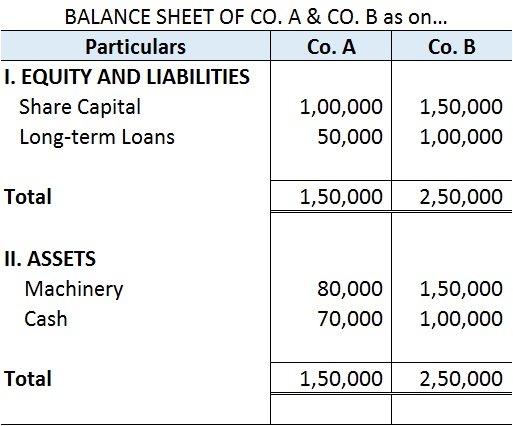
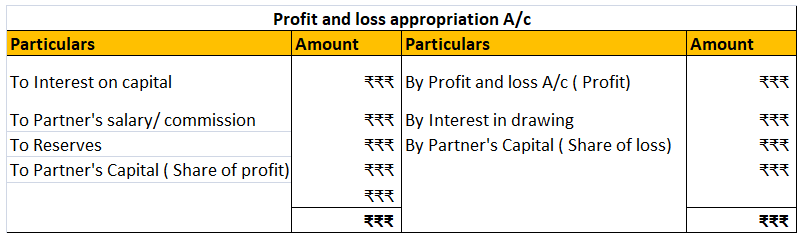
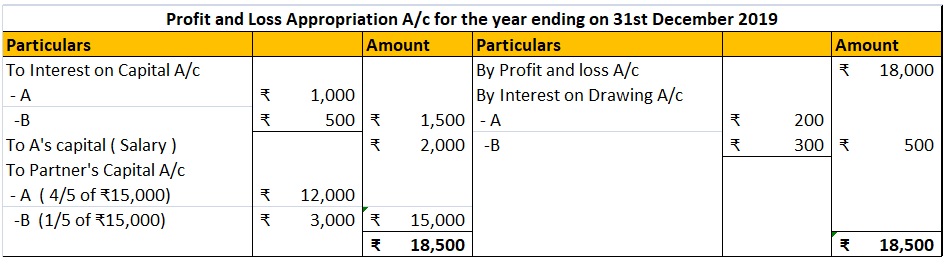


Definition Gross profit is the excess of the proceeds of goods and services rendered during a period over their cost, before taking into account administration, selling, distribution, and financial expenses. Gross profit and net profit are gross profit estimates of the profitability of a company. WhRead more
Definition
Gross profit is the excess of the proceeds of goods and services rendered during a period over their cost, before taking into account administration, selling, distribution, and financial expenses.
Gross profit and net profit are gross profit estimates of the profitability of a company.
When the result of this computation is negative it is referred to as gross loss
Formula :
Total Revenues – Cost Of Goods Sold
Net profit is defined as the excess of revenues over expenses during a particular period.
Net profit is to show the performance of the company.
When the result of this computation is negative it is called a net loss.
Net profit may be shown before or after tax.
Formula :
Total Revenues – Expenses
Or
Total Revenues – Total Cost ( Implicit And Explicit Cost )
Examples
Now let me explain to you by taking an example which is as follows :
In a business organization there were the following data given as purchases made Rs 73000, inventory, in the beginning, was Rs 10000, direct expenses made were Rs 7000, closing inventory which was Rs 5000, revenue from operation during the period was Rs 100000.
Then,
COST OF GOODS SOLD = Purchases + Opening Inventory + Direct Expenses – Closing Inventory.
= Rs ( 73000 + 10000+ 7000- 5000)
= Rs 85000
GROSS PROFIT = REVENUE – COST OF GOODS SOLD
= Rs ( 100000 – 85000 )
= Rs 15000
Now from the above question keeping the gross profit same if the indirect expenses of the organization are Rs 2000 and the other income is Rs 1000.
Then,
NET PROFIT = GROSS PROFIT – INDIRECT EXPENSES + OTHER INCOMES
= Rs ( 15000 – 2000 + 1000)
= Rs 14000
Treatment
Treatment of gross profit and net profit is given as follows :
Gross profit
• Gross profit appears on the credit side of the trading account.
• Gross profit is located in the upper portion beneath revenue and cost of goods sold.
Net profit
• Net profit appears on the credit side of the profit and loss account.
• It is treated directly in the balance sheet by adding or subtracting from the capital.
Here is an extract of the trading and profit/loss account and balance sheet showing GROSS PROFIT & NET PROFIT :

See less