Depletion Amortization Depression
A cash flow statement is a statement showing the inflow and outflow of cash and cash equivalents during a financial year. Cash Flow Statements along with Income statements and Balance Sheet are the most important financial statements for a company. The Cash Flow Statement provides a picture to the sRead more
A cash flow statement is a statement showing the inflow and outflow of cash and cash equivalents during a financial year. Cash Flow Statements along with Income statements and Balance Sheet are the most important financial statements for a company.
The Cash Flow Statement provides a picture to the shareholders, government, and the public of how the company manages its obligations and fund its operations. It is a crucial measure to determine the financial health of a company.
The Cash Flow Statement is created from the Income Statement and the Balance Sheet. While Income Statement shows money engaged in various transactions during the year, the Balance Sheet presents information about the opening and closing balances.
The primary objective of a Cash Flow Statement is to present a record of inflow and outflow of cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities through various activities of a company.
Various activities in a company can be broadly classified into three parts or heads:
- Cash Flow from Operating Activities: it represents how money from regular business activities is derived and spent. It includes Net Profit from Income Statement after adjusting for tax and extra-ordinary activities. Items included in Operating Activities are adjustments in Working Capital. If current liabilities are paid or current assets are bought it means outflow of cash, hence it is deducted and if liabilities are increased or assets are sold it means the inflow of cash, hence it is added. Operating Activities take into account taxation, dividend, depreciation, and other adjustments.
- Cash Flow from Investing Activities: it represents aggregate inflow or outflow of cash due to various investments activities that the company was engaged in. Purchase and sale of non-current assets like fixed assets and long-term investments are considered under this head. If there is an investment made, it means outflow of cash, hence it is deducted and if there is an investment sold it means the inflow of cash, and hence it is added.
- Cash Flow from Financing Activities: it represents the activities that are used to finance a company’s operations, like, issue of cash or debentures, paying dividends and interest, long-term borrowing taken by a company, etc. If these are paid, it means outflow of cash and is hence deducted and if they are acquired, it means the inflow of cash and hence ae added.
Cash Flow Statements also present a picture of the liquidity of the company and are therefore used by the management of a company to take decisions with the help of the right information.
Cash Flow Statements are a great source of comparison between a company’s last year’s performance to its current year or with other companies in the same industry and hence, helps shareholders and potential investors to make the right decisions.
It also helps to differentiate between non-cash and cash items; incomes and expenditures are divided into separate heads.
See less

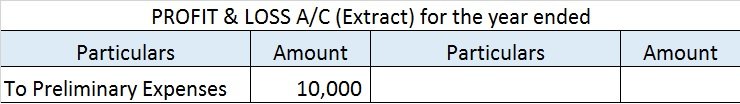
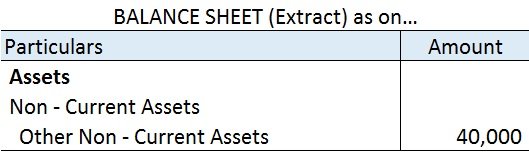

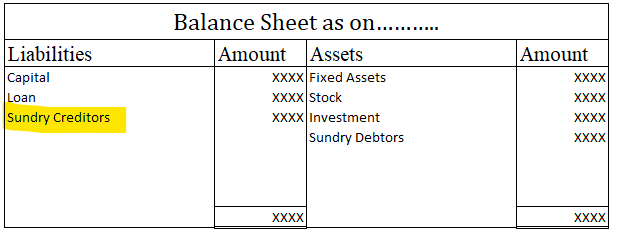
The correct option is 2. Amortization. Depreciation in spirit is similar to Amortization because both depreciation and amortization have the same characteristics except that depreciation is used for tangible assets and amortization for intangible assets. To make it clear, intangible assets are thoseRead more
The correct option is 2. Amortization.
Depreciation in spirit is similar to Amortization because both depreciation and amortization have the same characteristics except that depreciation is used for tangible assets and amortization for intangible assets.
To make it clear, intangible assets are those assets that cannot be touched i.e. they are not physically present. For example, goodwill, patent, trademark, etc. Hence, these assets are amortized over their useful life and not depreciated.
Example for Amortizing intangible assets: A manufacturing company buys a patent for Rs 80,000 for 8 years. Assuming that the residual value of the patent after 8 years to be zero.
The depreciation to be written off will be
Yearly Depreciation = Cost of the patent – Residual value / Expected life of the asset.
= 80,000 – 0 / 8
= Rs 10,000 every year.
Whereas, tangible assets are those assets that can be touched i.e. they are physically present. For example, building, plant & machinery, furniture, etc. Hence, these assets are depreciated over their useful life and not amortized.
Example of Depreciating tangible asset: A manufacturing company bought machinery for Rs 8,10,000 and its estimated life is 8 years, scrap value being Rs 10,000.
The depreciation to be written off will be
Yearly Depreciation = Cost of machinery – Scrap value / Expected life of the asset.
= 8,10,000 – 10,000 / 8
= 8,00,000 / 8
= Rs 1,00,000 every year.
See less