Partnership Firm Persons who have entered into a partnership with one another to carry on a business are individually called “Partners“; collectively called a “Partnership Firm”; and the name under which their business is carried on is called the “Firm Name” In simple words, A partnership is an agreRead more
Partnership Firm
Persons who have entered into a partnership with one another to carry on a business are individually called “Partners“; collectively called a “Partnership Firm”; and the name under which their business is carried on is called the “Firm Name”
In simple words, A partnership is an agreement between two or more people who comes together to run a business on a partnership deed, which is called a Partnership firm. A Partnership Deed is a written agreement between partners who are willing to form a Partnership Firm. It is also called a Partnership Agreement.
It has no separate legal entity which cannot be separated from the members. It is merely a collective name given to the individuals composing it. This means, a partnership firm cannot hold property in its name, and neither it can sue nor be sued by others.
Contents of a Partnership Deed
A Partnership Deed shall mainly include the following contents:
- Name of the Partnership firm
- Address of the Partnership firm
- Details of all the Partners
- Date of commencement of the Business
- The amount of capital contributed by each of the partners forming the Partnership firm
- The Profit sharing ratio (The Business profit shared among the partners on a ratio basis)
- The rate or amount of Interest on Capital & the rate or amount of Interest on drawings to each partner respectively.
- The salary is payable to each of the partners of the firm.
- The rights, duties, and power of each partner of the firm.
- The duration of the existence of the firm
Types of Partners
The following are the various types o partners
- Working partner or Active partner
- Sleeping partner
- Limited partner
- Partner in profit only
- Nominal or quasi partner
- Minor as a partner
Types of Partnership Firms
There are four types of partnership which are as below.
- General Partnership
- Limited Partnership
- Partnership at will
- Particular Partnership
Essential characteristics of a partnership firm
- Two or More persons: There must be at least two persons to form a partnership. A person cannot enter into a partnership with himself. The maximum number of persons in a partnership should not exceed 50.
- Agreement between partners: There must be an agreement between the parties in a partnership. The relation of partnership arises from the formation of a contract i.e., Partnership deed.
- Mutual Agency: Partnership business can be carried on by all the partners or by any of them acting on behalf of the others. in simple words, every partner is an agent to the other partners and of the form. Each partner is liable for acts performed by other partners on behalf of the firm.
- Registration of Firm: Registration of a partnership firm is not compulsory under the Act. The only document or even an oral agreement among partners required is the ‘partnership deed’ to bring the partnership into existence.
- Unlimited Liability: the liability of the partners is unlimited for the debts of the firm. In case the assets of the firm are insufficient to pay the debts in full, the personal property of each partner can be attached to pay the creditors of the firm.
- Non-Transferability of interest: there is a restriction in the transfer of shares of profits of the partnership without the prior consent of all other partners.
- Sharing of profits: The profits must be distributed among the partners in an agreed ratio. Similarly, losses should be shared among the partners.
- Lawful Business: The business carried on by the partners must be lawful. Illegal acts such as theft, dacoity, smuggling, etc., cannot be called partnerships.
- Utmost good faith: A partner must observe utmost good faith in all dealings with his co-partners. He must render true accounts and make no secret profits from the business.
See less


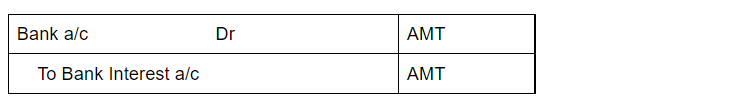
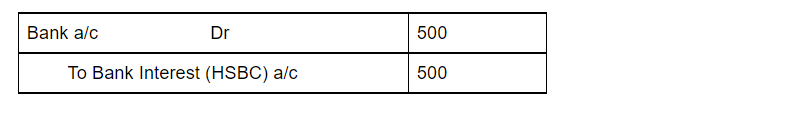
Business commencement with cash The term 'started the business with cash' is basically the commencement of business. In order to start any business, a certain sum of money has to be invested by the owner, which is known as the business's capital in accounting. Commencement of business refers to theRead more
Business commencement with cash
The term ‘started the business with cash’ is basically the commencement of business. In order to start any business, a certain sum of money has to be invested by the owner, which is known as the business’s capital in accounting.
Commencement of business refers to the starting or beginning of the business. In companies, it’s a declaration issued by the company’s directors with the registrar stating that the subscribers of the company have paid the amount agreed. In a sole proprietorship, the business can be commenced with the introduction of any asset such as cash, stock, furniture, etc.
Therefore, we may also call it the first journal entry of business because generally, people tend to start the business with cash rather than something else.
Journal entry
Explanation via rules
As per the golden rules of accounting, the cash a/c is debited as the rule says “debit what comes in, credit what goes out.” Whereas the capital a/c is credited because “debit all expenses and losses, credit all incomes and gains”
As per modern rules of accounting, cash is a current asset, and assets are debited when they increase. Whereas, on the increment on liabilities, they are credited, therefore, capital a/c is credited.
See less