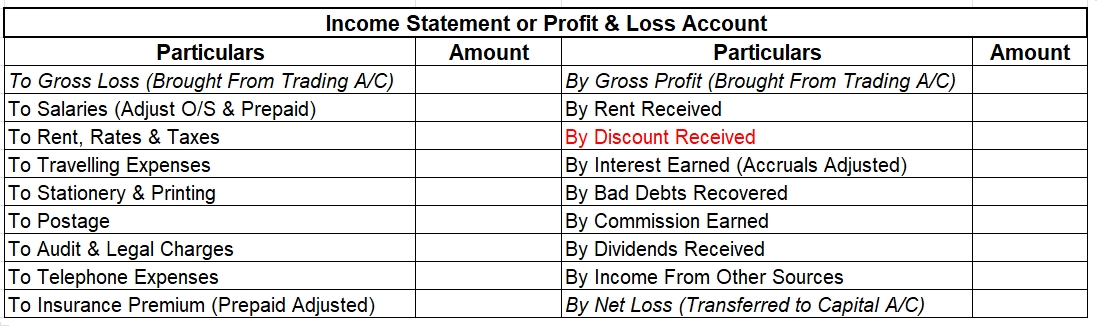
The profit earned by an entity is determined through the profit and loss account. All the expenses are recorded on the debit side of the profit and loss account while all the incomes are recorded on the credit side. The profit is shown as the credit balance of profit and loss A/c. When the sum of itRead more
The profit earned by an entity is determined through the profit and loss account. All the expenses are recorded on the debit side of the profit and loss account while all the incomes are recorded on the credit side.
The profit is shown as the credit balance of profit and loss A/c. When the sum of items on the debit side of a profit and loss account is less than the sum of those on the credit side, it implies profit while when the sum of the items on the credit side is less than the sum of those on the debit side, it implies a loss for the entity.
The Reason for Credit
Profit is recorded as an increase in equity
To understand the reason why profit is recorded as a credit balance, we must first understand the basic principle of debit and credit.
The basic principle of debits and credits is that debits increase asset accounts and decrease liability and equity accounts while credits decrease asset accounts and increase liability and equity accounts.
The revenue that a company earns is credited to the income account and increases equity.
The expenses that a company incurs to earn that revenue are debited to the expense account and decrease equity.
The difference between revenue and expenses is the profit, which is recorded as an increase in equity.
Increase in equity due to revenue – decrease in equity due to expense = profit
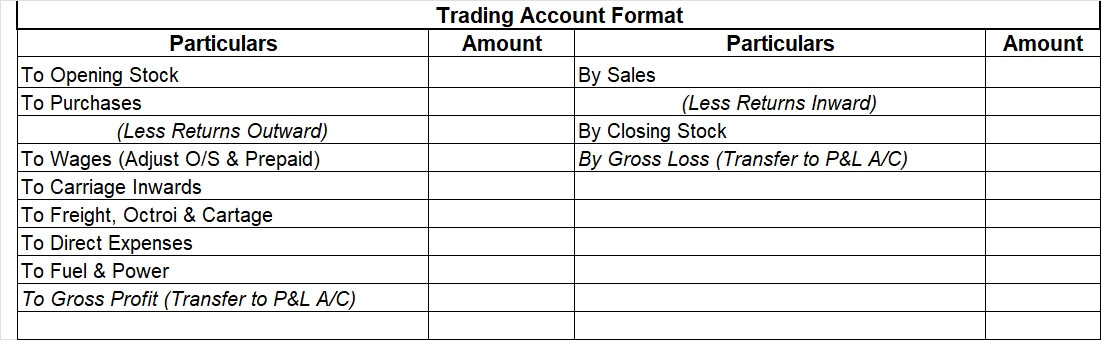
Gross Profit Vs Net Profit
Revenue is the total income that a business or profession earns. Profit is the excess revenue that remains after reducing all expenses from it.
Gross profit is the profit that a company earns after reducing the cost of goods sold from sales revenue while net profit is the profit that a business earns after reducing the total of all its direct and indirect expenses from its direct as well as indirect allowable business income.
Conclusion
The basic principle of debit and credit governs the classification of profit as a debit or credit. Since profit increases our equity, it is a credit.
In the case of a company, it belongs to the shareholders. It is usually recorded in the retained earnings account. Profit can be reinvested in the business or can be distributed as a dividend. In the case of a sole proprietorship, the profit belongs to the owner and is recorded in the owner’s capital account.
See less
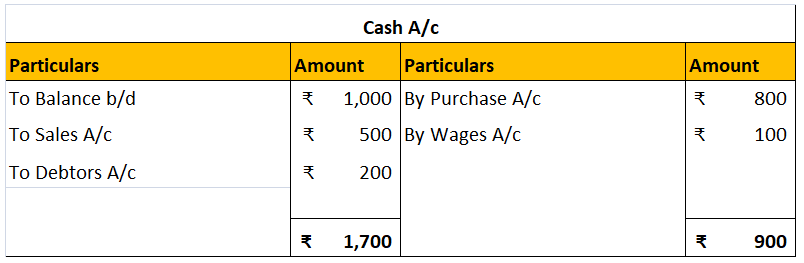
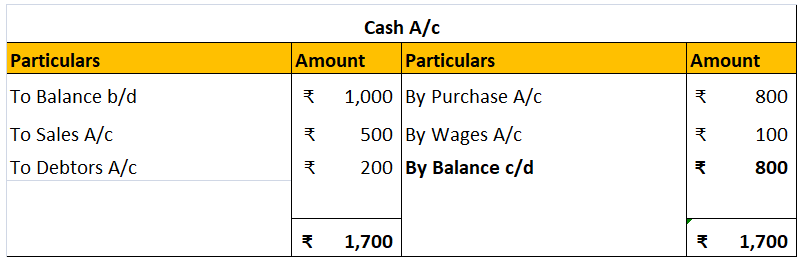
A cash flow statement presents the changes in the cash and cash equivalents of a business. It classifies the cash flow items into either operating, investing, or financing activities. Unlike a balance sheet that provides information about the company on a particular date, a cash flow statement proviRead more
A cash flow statement presents the changes in the cash and cash equivalents of a business. It classifies the cash flow items into either operating, investing, or financing activities. Unlike a balance sheet that provides information about the company on a particular date, a cash flow statement provides information about the flow of cash over a period of time.
OBJECTIVE
Information obtained through cash flow statements is aimed to assess the ability of a business to generate cash and at the same time, maintain liquidity. Therefore, important economic decisions can be made by evaluating these cash flow statements.
Cash Flow statements are categorized into
Importance of Cash Flow
A cash flow statement gives us knowledge about the liquidity and solvency of the company. These are necessary for the survival and expansion of the company. It also helps in predicting future cash flows by using information from previous cash flows. It also helps in comparison between companies which shows the actual cash profits.

See less