Introduction A capital reduction account is an account used to pass entries related to the internal reconstruction of a company. During reconstruction, paid-up capital reduced is credited to this account; hence its name is capital reduction account. It is also known as the reconstruction account. TyRead more
Introduction
A capital reduction account is an account used to pass entries related to the internal reconstruction of a company. During reconstruction, paid-up capital reduced is credited to this account; hence its name is capital reduction account. It is also known as the reconstruction account.
Type of account
A capital reduction account is a temporary account open just to carry out internal reconstruction. It represents the sacrifices made by the shareholders, debenture holders and creditors. Also, any appreciation in the value of assets is credited to this account. It is closed to capital reduction when internal reconstruction is completed.
Entries passed through capital reduction account
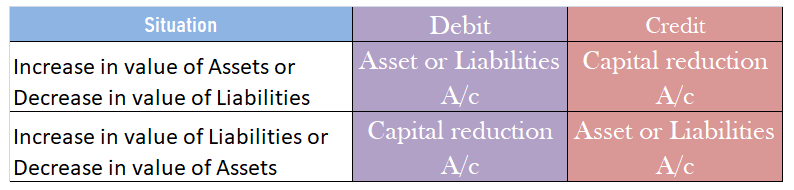
When paid-up capital is cancelled.
When paid-up capital is cancelled, the share capital account is debited and the capital reduction account is debited as share capital is getting reduced.
| Share Capital A/c | Dr. | Amt |
| To Capital Reduction A/c | Cr. | Amt |
When assets and liabilities are revalued
At the time of internal reconstruction, the gain or loss on revaluation is transferred to the capital reduction account instead of the revaluation reserve.
Writing off of accumulated losses and intangible assets
The credit balance of the capital reduction account is used to write off the accumulated losses and intangible assets like goodwill, patents etc which are unrepresented by capital. The capital reduction account is debited and profit and loss account and intangible assets accounts are credited.
| Capital Reduction A/c | Dr. | Amt |
| To Profit and loss A/c | Cr. | Amt |
| To Goodwill/ Patents A/c | Cr. | Amt |
Treatment in books of account
The balance in the capital reduction account, whether debit or credit, it is transferred to the capital reduction account. Hence, it doesn’t appear on the balance sheet.
See less
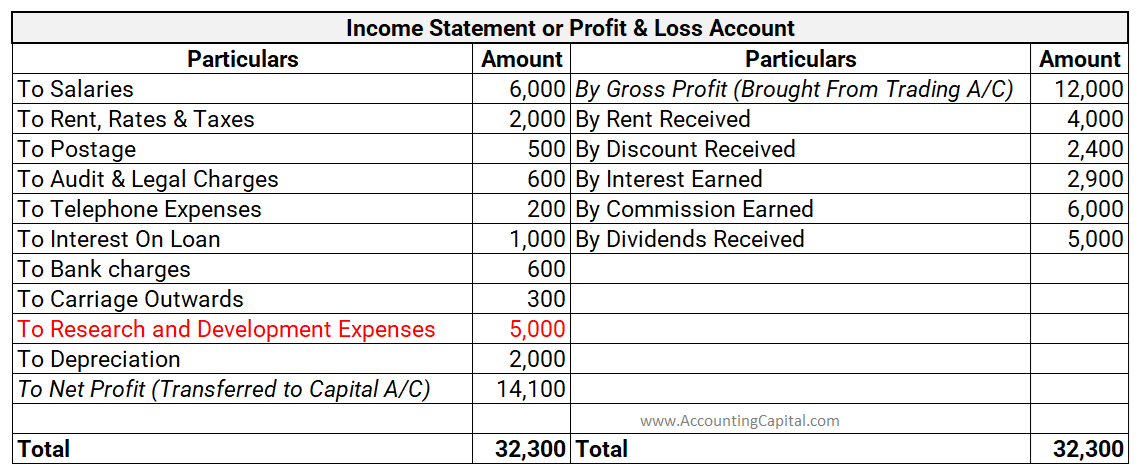


Sales return shows the sale price of goods returned by customers. It is deducted from sales or gross sales in the income statement. It is a contra revenue account that represents returns from the customers and deductions to the original selling price, in case of any defective product received by theRead more
Sales return shows the sale price of goods returned by customers. It is deducted from sales or gross sales in the income statement.
It is a contra revenue account that represents returns from the customers and deductions to the original selling price, in case of any defective product received by the customer or any other manufacturing default.
Sales allowances arise when any customer accepts the product at a lower price than the original price or, in other words, a reduction in the price charged by a seller, due to any problem related to the sold product like a quality issue, an incorrect price charged or shipment issue.
Sales allowances are created before the final billing is paid by the buyer.
Journal entry for sales return and allowances:
See less