The journal entry for the closing stock is passed at the year-end as closing stock is the inventory held by a business at the end of its accounting period. However, the entry for recording closing stock depends on how it is treated in the books of accounts. The two types of the accounting treatmentRead more
The journal entry for the closing stock is passed at the year-end as closing stock is the inventory held by a business at the end of its accounting period. However, the entry for recording closing stock depends on how it is treated in the books of accounts.
The two types of the accounting treatment of closing stock are as follows:
- Closing stock is not shown in the Trial Balance.
- Closing stock is shown in the Trial Balance.
Closing stock is not shown in the Trial Balance:
As per this treatment, the closing stock is not shown in the Trial Balance because it is already a part of the purchases of the business. Showing it in the Trial Balance would lead to a double effect. This will not give us accurate profit/loss at the end of the year.
The closing stock is transferred to Trading A/c by passing a closing entry.

Closing stock is an asset. It is debited because there is an increase in the assets. Trading A/c is credited because of the Matching concept as the value of the closing stock is adjusted against the cost of goods sold.
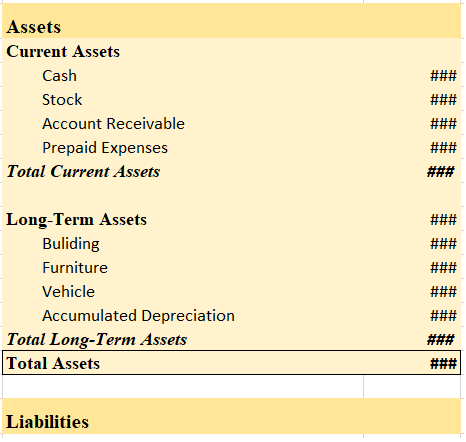
At the end of the year, it is shown on the Asset side of the Balance Sheet, under the head Current Assets and sub-head Inventory.
For example,
ABC Ltd. at the beginning of the year had an opening inventory of 20,000. During the year, purchases worth 5,000 were made and goods worth 10,000 were sold. At the end of the year, the value of the closing stock will be 15,000 (20,000 + 5,000 – 10,000).
Now the closing stock worth 15,000 will be recorded through this journal entry:
| Closing Stock A/c | 15,000 |
| To Trading A/c | 15,000 |
| (Being closing stock worth 15,000 transferred to Trading A/c) |
Closing stock is shown in the Trial Balance:
This scenario is possible only when the closing stock is adjusted against purchases. By adjusting against purchases, the double effect of showing both purchases and closing stock in Trial Balance is eliminated.
The following entry is recorded to adjust closing stock against purchases.

Closing Stock is debited as there is an increase in the asset. Purchase A/c is credited because of the Matching concept.
After recording the adjustment entry, the closing stock is shown on the debit column of the Trial Balance. It is not shown in the Trading A/c as it is already adjusted against purchases. In the Balance Sheet, it is shown as a Current Asset.
See less

Capital Expenditure Capital expenditure refers to the money a business spends to buy, maintain, or improve the quality of its assets. Capital expenditures are the expenses incurred by an organization for long-term benefits, i.e on the long-term assets which help in improving the efficiency or capaciRead more
Capital Expenditure
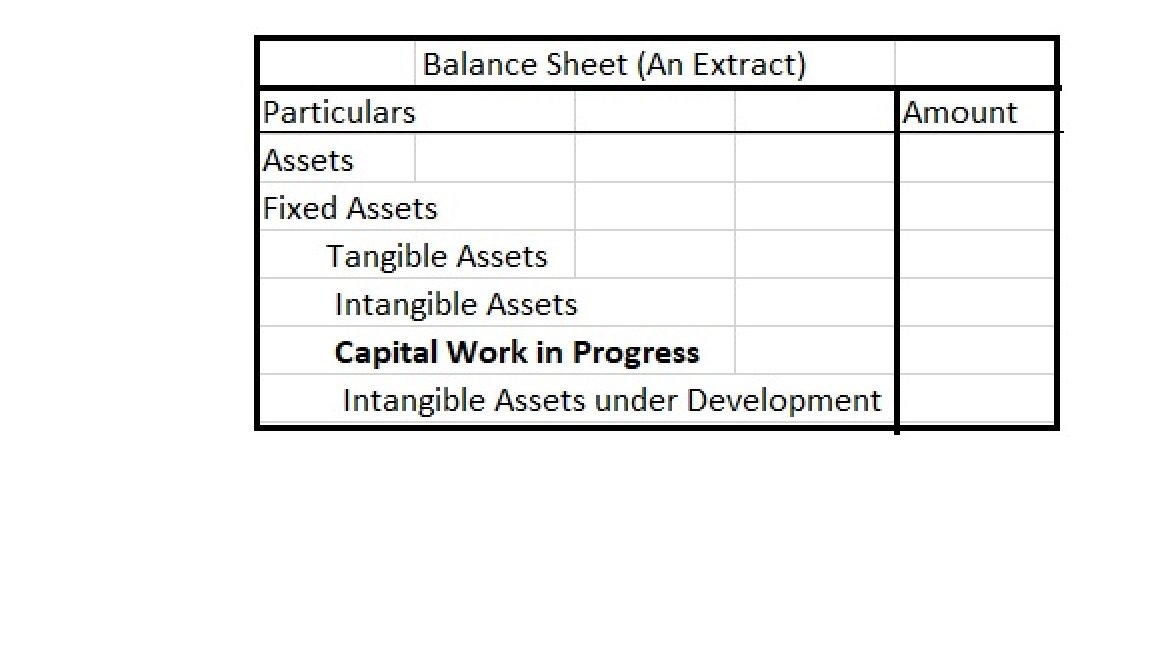
Capital expenditure refers to the money a business spends to buy, maintain, or improve the quality of its assets. Capital expenditures are the expenses incurred by an organization for long-term benefits, i.e on the long-term assets which help in improving the efficiency or capacity of the company. These expenses are borne by the company to boost its earning capacity.
The investment done by the companies on assets is capital in nature and through capital expenditure, the company may use it for acquiring new assets or may use it in the maintenance of previous ones. These expenditures are added to the asset side of the balance sheet.
Example: Purchase of machinery, patents, copyrights, installation of equipment, etc.
Revenue Expenditure
Revenue expenditure refers to the routine expenditures incurred by the business to manage day-to-day expenses. They are incurred for a shorter duration and are mostly limited to an accounting year. These expenses are borne by a company to sustain its profitability. These expenditures are shown in the income statement.
These expenditures do not increase the revenue but stay maintained. These expenses are not capitalized.
They are divided into two sub-categories:
Example: Wages, salary, insurance, rent, electricity, taxes, etc.
See less