The correct answer is 4. Not shown in Branch Account. The value of depreciation of fixed assets will be not shown in the branch accounting because the opening value of the asset is recorded at the start of the period on the debit side and the closing value of the asset is shown on the credit side atRead more
The correct answer is 4. Not shown in Branch Account.
The value of depreciation of fixed assets will be not shown in the branch accounting because the opening value of the asset is recorded at the start of the period on the debit side and the closing value of the asset is shown on the credit side at the end of the period.
The difference between the opening and closing values of the asset is the value of depreciation which is automatically charged. In this case, if depreciation is also shown it will be counted twice.
Example:
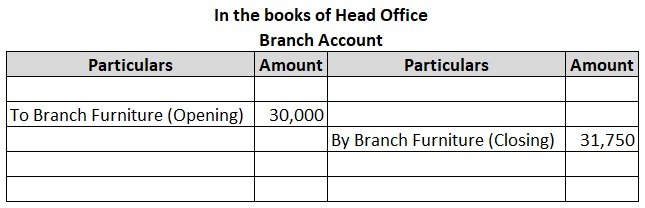
XYZ Ltd purchased furniture for one of its branches on 1st January. Following are the details of the purchase:
| Furniture as on 1st January | $30,000 |
| Furniture purchased on 1st June | $5,000 |
Depreciation is provided on furniture at @10% per annum on the straight-line method.
| Woking Notes: | Amt |
| i. Depreciation on furniture: | |
| On $30,000 @10% p.a for full year | 3,000 |
| On $5,000 @10% p.a for 6 months | 250 |
| 3,250 | |
| ii. Branch Furniture as of 31 Dec: | |
| Furniture as of 1 January | 30,000 |
| Add: Addition made during the year | 5,000 |
| 35,000 | |
| Less: Depreciation | (3,250) |
| 31,750 |
As additional furniture was purchased after 6 months, depreciation will be charged on that and the total depreciation of 3,250 will be charged on the furniture of $35,000 ($30,000+$5,000) and the difference will be the closing balance which will be shown in the branch account on the credit side.
The depreciation amount will not be shown in the Branch Account as the difference between the opening and closing values of the furniture reflects the value of depreciation. If depreciation is shown in the account it will be counted twice.
See less


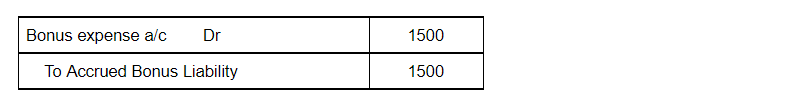 The bonus expense account is debited because according to the modern rule of accounting “Increase in expense is debited”. Accrued bonus liability is credited because according to the rule of accounting, “Increase in liability is credited”.
The bonus expense account is debited because according to the modern rule of accounting “Increase in expense is debited”. Accrued bonus liability is credited because according to the rule of accounting, “Increase in liability is credited”.
In trial balance, the treatment of the general reserve is that it is presented on the credit side. A trial balance is a statement prepared to check the arithmetical accuracy of the books of accounts. It features the closing balances of all the assets, liabilities and equity of a business. General reRead more
In trial balance, the treatment of the general reserve is that it is presented on the credit side.
A trial balance is a statement prepared to check the arithmetical accuracy of the books of accounts. It features the closing balances of all the assets, liabilities and equity of a business.
General reserve is a free reserve created out of revenue profits of a business to meet future needs and uncertainties. By free reserve, we mean dividends can be freely declared and distributed out of it.
Since the general reserve is an internal liability i.e. liability to the owner or owners or the business, it has a credit balance and is hence shown on the credit side of the trial balance.
See less