Ledger posting As we know, a business records all of its transactions in the journal. After the transactions are recorded in the journal, they are posted in the principal book called ‘Ledger’. Transferring the entries from journals to respective ledger accounts is called ledger posting or posting toRead more
Ledger posting
As we know, a business records all of its transactions in the journal. After the transactions are recorded in the journal, they are posted in the principal book called ‘Ledger’. Transferring the entries from journals to respective ledger accounts is called ledger posting or posting to the ledger accounts. Balancing of ledgers is carried out to find differences at the year’s end.
Posting to the ledger account means entering information in the ledger, and respective accounts from the journal for individual records. The accounts that are credited are posted to the credit side and vice versa.
Ledger maintenance is done at the end of an accounting period and it’s maintained to reflect a permanent summary of all the journal accounts. In the end, all the accounts that are entered and operated in the ledger are closed, totaled, and balanced. Balancing the ledger means finding the difference between the debit and credit amounts of a particular account.
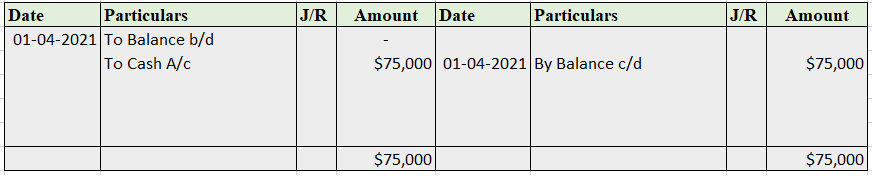
While posting to the ledger account, suppose goods were bought for cash. While passing the journal entry, we’ll be debiting the purchases a/c and crediting the cash a/c by stating it as, ‘To Cash A/c’.
Now, this entry will be affecting both the purchases account and the cash account. In the cash account, we’ll be debiting purchases. Whereas in the purchases account, we’ll be crediting the cash. That’s how it works in the double-entry bookkeeping system of accounting.
Example
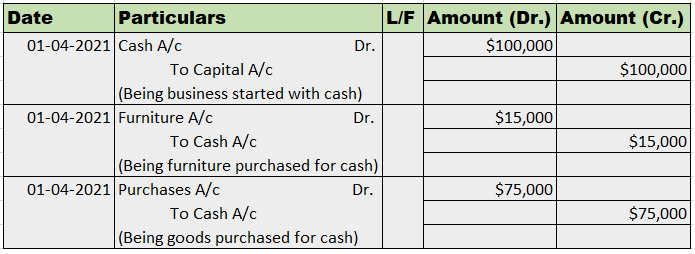
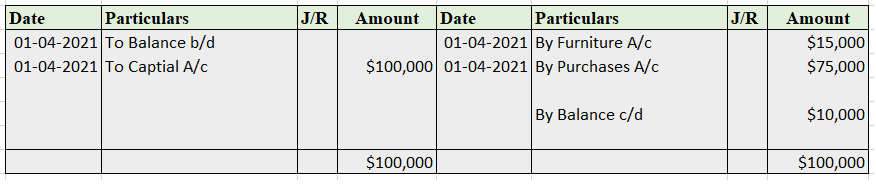
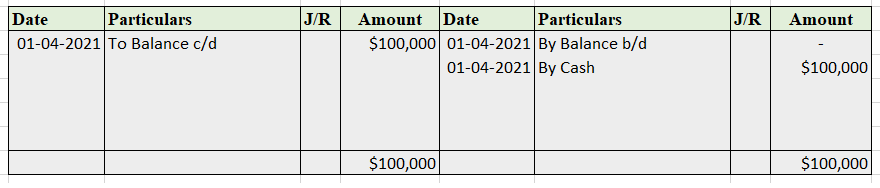
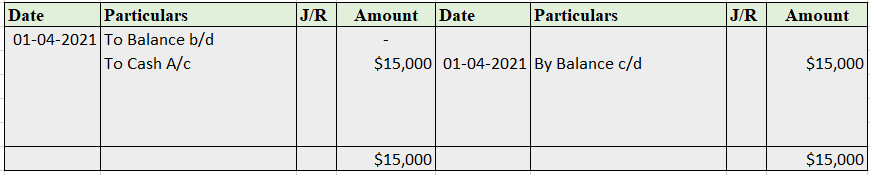
Mr. Tony Stark started the business with cash of $100,000 on April 1, 2021. He bought furniture for business for $15,000. He further purchased goods for $75,000.
Now, we’ll be journalizing the transactions and posting them into the ledger accounts.
Journal Entries
Posting to Ledger Account
Cash A/c
Capital A/c
Furniture A/c
Purchases A/c
See less


Meaning of lease A lease is an agreement or a contract in which the right to use an asset like land, building, or machinery is given by one party to the other party for a fixed period of time against the consideration of a single payment or a series of payments. There are two parties in a lease agreRead more
Meaning of lease
A lease is an agreement or a contract in which the right to use an asset like land, building, or machinery is given by one party to the other party for a fixed period of time against the consideration of a single payment or a series of payments.
There are two parties in a lease agreement:
This is similar to a rent agreement or contract. The only difference between lease and rent is duration. A rent agreement is generally for less than 12 months while a lease agreement is for more than 12 months like 5 years or 10 years, sometimes even for like 99years.
Type of lease
There are two types of lease:
Operating lease
Finance lease
Difference between operating lease and finance lease in tabular format
See less