1) Cash Book 2) Statement 3) Journal 4) None of these
The main objective of depreciation is to calculate net profit. Depreciation is an expense allowed on the fixed assets of an entity to provide for the cost of benefit utilized by the entity in that particular year. Since the such assets are used for more than one financial year, profits for the furthRead more
- The main objective of depreciation is to calculate net profit.
Depreciation is an expense allowed on the fixed assets of an entity to provide for the cost of benefit utilized by the entity in that particular year. Since the such assets are used for more than one financial year, profits for the further years would be misstated if such depreciation expense is not provided for.
Further, depreciation in no way shows previous profits or satisfies the tax department and a reduction in tax is secondary since it will only be allowed if charged in the profit & loss account. Thus, B is the correct answer.
2. Depreciation is generated due to wear and tear.
Depreciation is provided for to compensate for the wear and tear of the asset while being used by the entity. Depreciation is not generated due to increase in the value of liability, decrease in capital or decrease in the value of assets. Rather the vice versa is true, that is an increase in liability, decrease in capital and decrease in asset is created due to depreciation.
Thus, C is the correct answer.
3. The purpose of making a provision for depreciation in the accounts is to charge the cost of fixed assets against profits.
Fixed assets are long term assets with useful life of more than one accounting year and therefore the full cost of such assets are not provided for in the year of purchase rather a fixed portion is charged every year in the profit and loss account.
Thus, A is correct and others are incorrect.
4. According to the straight line method of depreciation, the depreciation remains constant.
In the straight line method of depreciation, depreciation is calculated on the historical or purchase cost of the asset and the same amount is charged every year till the useful value of the asset, thus depreciation remains constant.
Also, depreciation decreases each year in case of written down value method but depreciation can never increase. Thus, A is the correct answer.
5. Total amount of depreciation of an asset cannot exceed its depreciable value.
The depreciable value is the purchase cost of the asset less the scrap value. The total amount of depreciation can never exceed the depreciable value since depreciation is allowed on an asset till its useful life at a certain percentage. Even when the value of the asset becomes nil, no further depreciation would be charged and total depreciation would be equal to depreciable value but obviously cannot be more.
Thus, A is the correct answer and other are wrong.
6. According to fixed installment method, the depreciation is calculated on original cost.
In the fixed installment method, also known as the straight line method, depreciation is calculated on the basis of the original or purchase cost of the asset using the formula-
Depreciation = (Original cost – Scrap value)/Useful life of asset
Thus, B is the correct answer.
7. Salvage value means estimated disposal value.
Salvage value is the value of the asset that can be realized by the entity on its sale after the useful life of the asset has been exhausted and is now obsolete for the entity.
Salvage value is not definite but an estimation. Salvage value can be positive or nil but not negative. Thus, D is the correct option.
8. Depreciation is calculated under diminishing balance method, based on book value.
Under the diminishing value method, the depreciation is calculated at a certain percentage of the book value of the asset which is calculated after providing for depreciation in the previous year.
Depreciation cannot be calculated on scrap value since it is the disposable value of the asset and depreciation on original value is calculated under straight line method. Thus, B is the correct option.
9. Depreciation amount charged on a machinery will be debited to depreciation account.
Depreciation is an expense and depreciation account will be debited since depreciation is a nominal account, as per traditional method, and all expenses are debited. Also, as per modern rules of accounting, increase in expenses are debited.
When depreciation is charged there is a decrease in the value of assets therefore machinery account will be credit also depreciation cannot be classified under repair account or cash account heads. Thus, C is the correct option.
10. In accounting, becoming out of date or obsolete is known as obsolescence.
Amortization means decrease in the value of intangible assets of an entity. Depletion means exhaustion of existing wasting assets such as coal mines. Physical deterioration means fall in value of asset due to physical damage to the asset. Therefore, the correct answer is Obsolescence.
See less
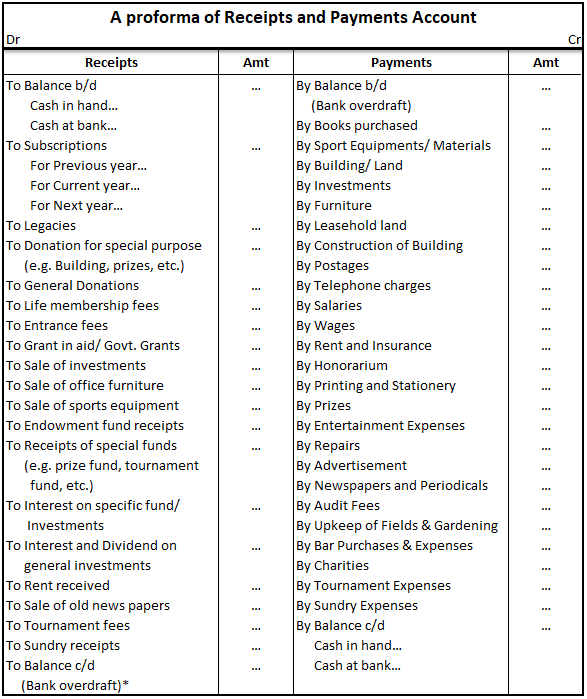
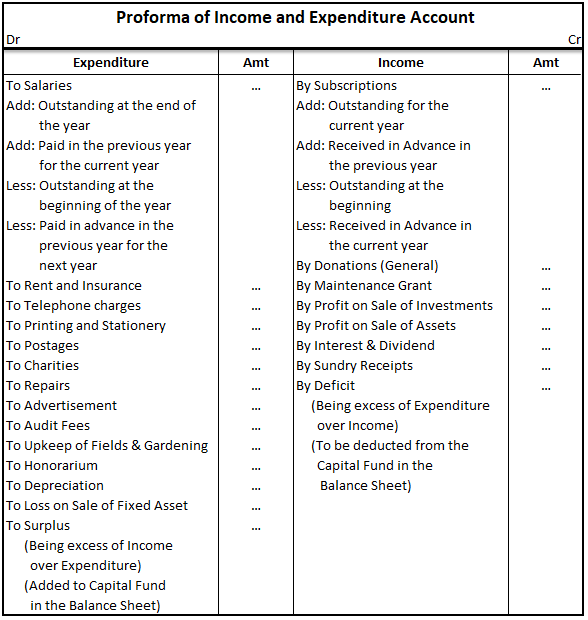
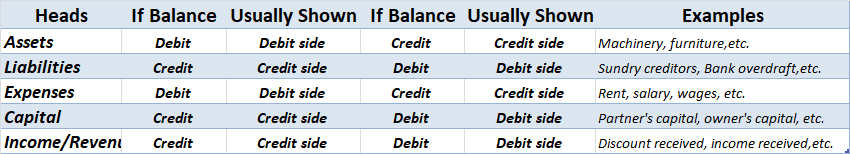
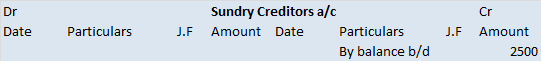
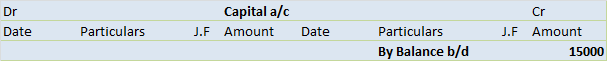
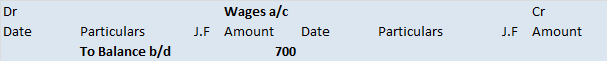
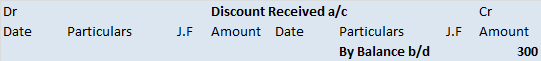
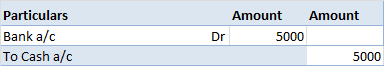
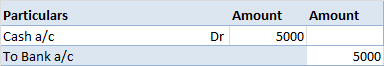
 The trial balance shows the opening balance of various accounts. Now posting them in ledger accounts.
The trial balance shows the opening balance of various accounts. Now posting them in ledger accounts.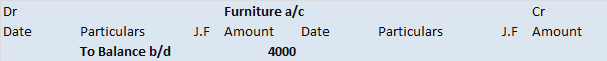
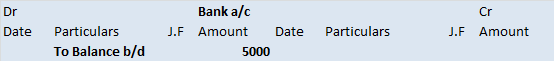
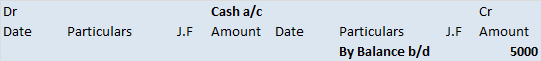

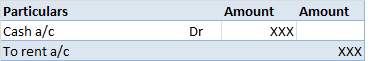
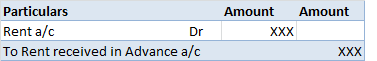
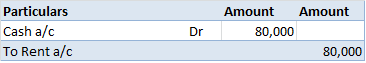
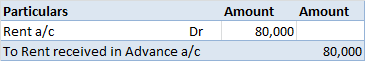
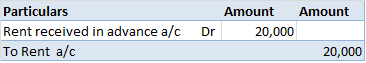
1) A simple petty cash book is like a cash book. Definition The term 'petty' means small. A simple petty cash book is identical to a cash book, maintained to record the small expenses of a business like stationery, postage, stamps, carriage, etc. The cash received by a petty cashier is recordRead more
1) A simple petty cash book is like a cash book.
Definition
The term ‘petty’ means small. A simple petty cash book is identical to a cash book, maintained to record the small expenses of a business like stationery, postage, stamps, carriage, etc. The cash received by a petty cashier is recorded on the debit/ receipt side whereas, the cash he pays is recorded on the credit/ payment side. The difference between the sum of the debit and credit items represents the balance of the petty cash in hand.
Format
Explanation
Cash Book – A simple petty cash book is recorded and maintained just like the cash book. Just like a cash book records all the major transactions of the business, a petty cash book only focuses on the expenses which are of little value. Just like the cash book is maintained by the accountant of the business, the petty cash book is maintained by the petty cashier.
Therefore, a petty cash book is like a sub-part of a cash book itself.
Statement – A statement in accounting terms refer to a report. They are prepared to show some accounting data and different types of statements show different perspectives of the company’s financial health and performance. For e.g Balance sheet, trial balance, cash flow statements, etc.
Thus, a petty cash book is not a part of statements in accounting.
Journal – A petty cash book is not a part of a journal as a journal entry records business transactions in the accounting system for an organization and is also called the building block of the double-entry accounting method. While a petty cash book is maintained to record the small expenses of a business that are of little value.
Therefore, 1) Cash book is the correct option.
See less