Whenever the proprietor/owner of a business withdraws cash or goods from the business for his/her personal use, we call it drawings. For example, Alex, proprietor of a soap manufacturing company, takes 50 pack of soaps costing 30 each for his personal use. So, 1,500 (50*30) will be considered as draRead more
Whenever the proprietor/owner of a business withdraws cash or goods from the business for his/her personal use, we call it drawings. For example, Alex, proprietor of a soap manufacturing company, takes 50 pack of soaps costing 30 each for his personal use. So, 1,500 (50*30) will be considered as drawings of Alex. One important thing to note here is whenever goods are withdrawn for personal use they are valued at cost.
Drawings are not an asset/liability/expense/income to the business. The drawings account is a contra-equity account. A contra-equity account is a capital account with a negative balance i.e. debit balance. It reduces the owner’s equity/capital.
Drawings being a contra-equity account has a debit balance, reducing the owner’s capital in the business. This is because withdrawals for personal use represent a reduction of the owner’s equity in the business.
Drawings are not shown in the Income Statement as they are neither an expense nor an income for the business. However, the following journal entries are passed to record drawings for the year:
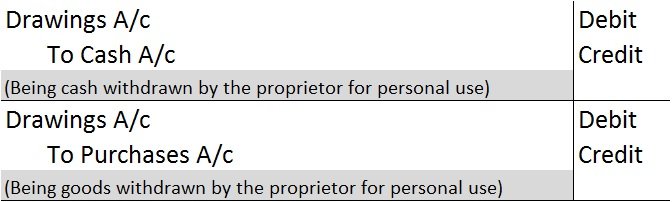
Drawings A/c is debited because it reduces the owner’s capital. Cash/Purchases A/c is debited as a withdrawal reduces the assets of the business.
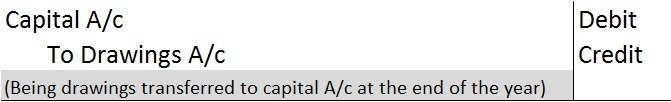
At the end of the year, drawings A/c are closed by transferring it to the owner’s capital A/c. We post the following entry to close the drawings A/c at the end of the year:
In the balance sheet, drawings are shown by deducting it from the owner’s capital A/c.
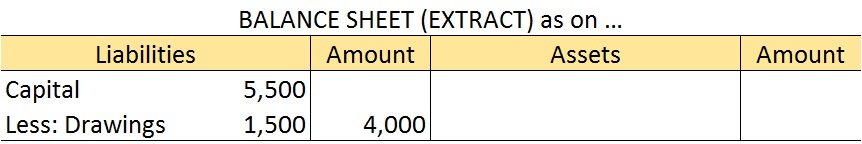
Let us take our earlier example of Alex. He withdrew soaps worth 1,500. At the end of the year, his capital was worth 5,500. The journal entry for recording the drawings is as follows:

In the balance sheet, drawings worth 1,500 are shown as follows:

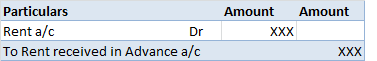
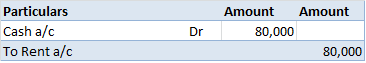
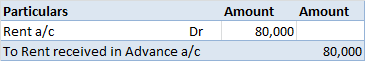
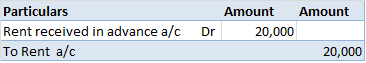
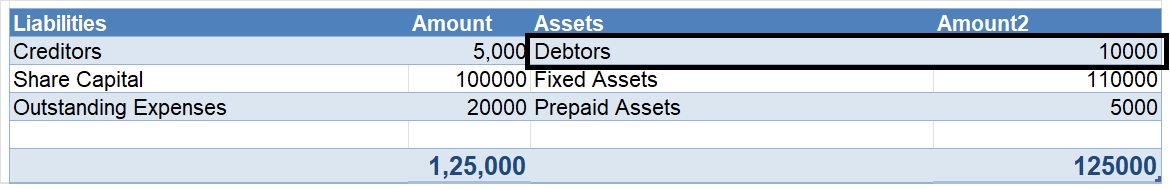

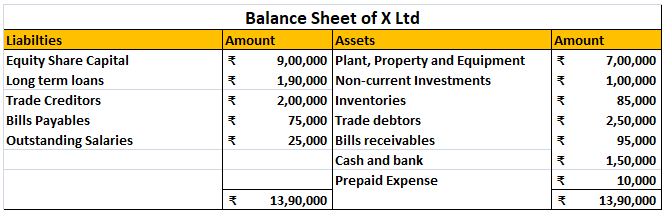

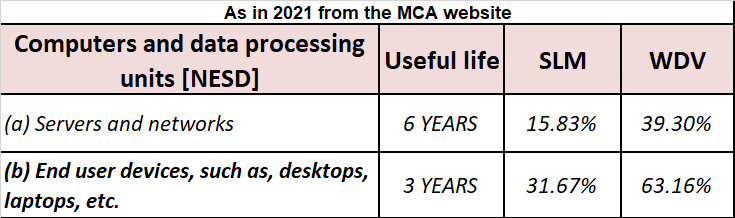
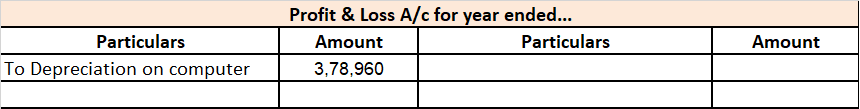
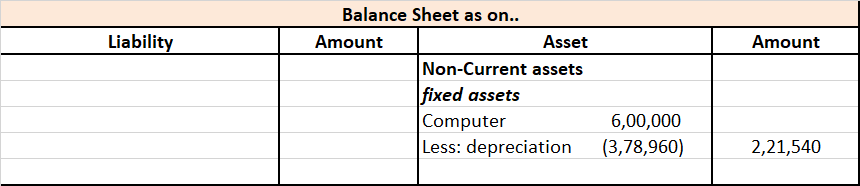
Revaluation of Assets is an adjustment made in the carrying value of the fixed asset in case the company finds there is a difference between the current price and the market value of the asset. Generally, the value of the asset decreases due to depreciation but in some cases like inflation in the ecRead more
Revaluation of Assets is an adjustment made in the carrying value of the fixed asset in case the company finds there is a difference between the current price and the market value of the asset. Generally, the value of the asset decreases due to depreciation but in some cases like inflation in the economy, it may increase. so, in order to know the correct value of the asset Revaluation is to be done.
Accounting standard allows two models.
Under the cost model, the carrying value of fixed assets equals their historical cost less accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses.
For Example, Amazon ltd purchased a Plant for 5,00,000 on January 1, 2010, with a useful life of 10 years, and uses straight-line depreciation.
Here, the journal entry would be passed as
As the useful life of the asset is 20 years, so the yearly depreciation would be
5,00,000/10 i.e. 50,000.
So the accumulated depreciation at the end of December 31, 2012, would be 50,000×2= 1,00,000 and
the carrying amount would be 5,00,000-1,00,000= 4,00,000.
Under the Revaluation method, the assets are revalued at their current market value. If there is an increase in the value of an asset, the difference between the asset’s market value and current book value is recorded as a revaluation surplus.
For Example, Amazon ltd purchased an asset two years ago at a cost of 2,00,000. Depreciation @ 10% under straight-line method.
Therefore, the accumulated depreciation for two years would be 40,000,
i.e. 20,000 for a year.
Carrying cost of the asset = 1,60,000
Assuming, the company revalues its assets and finds that the worth of assets is 1,85,000.
Under this method, the company needs to record 25,000 as a surplus.
Accounting entry for the above will be
Depreciation calculated during the third year would be based on the new carrying value of 1,60,000.
Therefore, Depreciation for the 3rd year= 1,60,000/3
= 53,333.33
Accounting entry:
Alternatively, the incremental depreciation due to the revaluation i.e. 13,333.33 can be charged to the revaluation surplus account.
In case, if there is a revaluation loss, the entries would be interchanged.
In case of admission of a partner, the new partner may not agree with the value of assets as stated in the balance sheet, with time the values may have arisen or may have fallen, so in order to bring them to their correct values revaluation is done so that the new partner doesn’t suffer.
Where the assets and liabilities are to be shown in the books at the revised (new) values after the admission of the new partner.
The accounting entries are
2. For a decrease in the value of an asset
3. For transfer of profit on revaluation i.e. if the total of credit side exceeds the debit side.
4. For transfer of loss on revaluation i.e. if the total of debit side exceeds the credit side.
Note: If the total of both sides is equal it signifies that there is no profit or loss on the revaluation of assets. Hence no entry is to be passed.
After preparing for the journal entry, a revaluation ledger account is also prepared wherein the accounts carrying a debit balance are transferred to the debit side and the accounts carrying a credit balance are transferred to the credit side.
In the case of retirement of a partner, the same journal entries are to be passed as in the case of Admission of a partner for revaluation of assets.
Generally, the value of an asset decreases with time but it may increase in certain circumstances especially in inflationary economies.
Conclusion
An entity should do the revaluation of its assets because revaluation provides the present value of assets owned by an entity and upward revaluation is beneficial for the entity and hence the company can charge more depreciation on upward revaluation and can get tax benefits.
See less