Introduction & Definition Firstly, let's see what the term 'petty cash book' means. The word ‘petty’ means small. A petty cash book is identical to a cash book, maintained to record the small expenses of a business like stationery, postage, stamps, carriage, etc. The cash received by a petty casRead more
Introduction & Definition
Firstly, let’s see what the term ‘petty cash book’ means. The word ‘petty’ means small. A petty cash book is identical to a cash book, maintained to record the small expenses of a business like stationery, postage, stamps, carriage, etc. The cash received by a petty cashier is recorded on the debit/ receipt side whereas, the money he pays is recorded on the credit/ payment side. The difference between the sum of the debit and credit items represents the balance of the petty cash in hand.
The reason the petty cash book is maintained is that it records small expenses that are inconvenient or too small to be registered in the cash book. This is also called a simple petty cash book. Just like a cash book is maintained by the accountant, the petty cash book is maintained by a petty cashier.
When it comes to the format, there are two types of petty cash book formats. They are-
- Simple Petty Cash Book
- Analytical Petty Cash Book
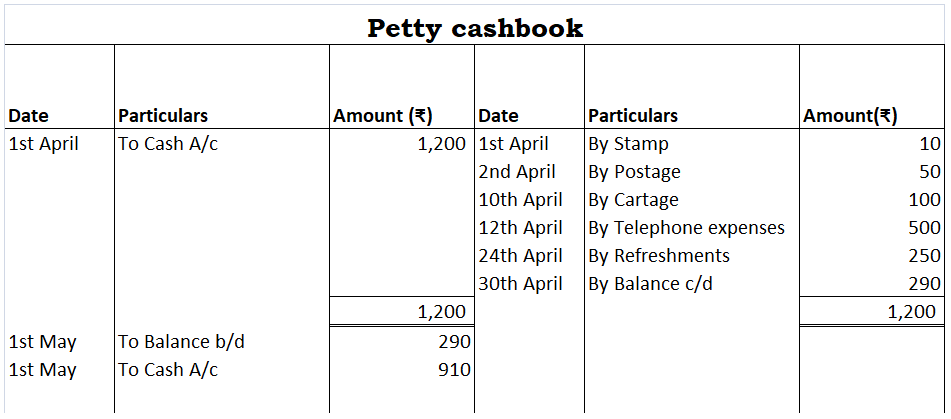
We have been discussing the simple petty cash book so far. Thus,
Format of Simple Petty Cash Book
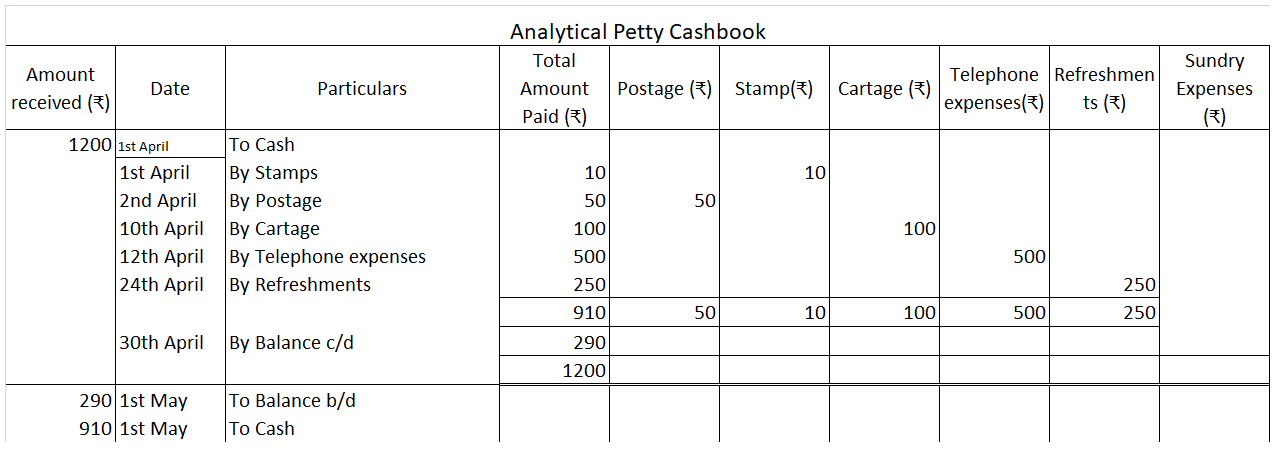
Analytical Petty Cash Book
The analytical petty cash book has numerous columns for the recording of monetary transactions. In the analytical petty cash book, there are pre-existing columns for the usual expenses that are recorded frequently in the business which makes it easier for a business that has daily expenses for food, stationery, postage, etc. They’ll be having individual columns. It has numerous columns in it for the recording of expenses in it.
The key advantages of an analytical petty cash book are-
- One of the major key advantages is that the analytical petty cash book due to its format and structure saves time.
- The other advantage is that it helps the business in easy comparisons.
- It requires lesser time in recording.
Format of Analytical Petty Cash Book
See less

In accounting, sales returns are the goods returned by the customer to the seller. This can be due to goods delivered is damaged or defective. A return can also be due to late delivery, or the wrong items being sent to the buyer. Sales return is a subsidiary book in which all the details are recordeRead more
In accounting, sales returns are the goods returned by the customer to the seller. This can be due to goods delivered is damaged or defective. A return can also be due to late delivery, or the wrong items being sent to the buyer.
Sales return is a subsidiary book in which all the details are recorded for the goods returned which were sold on credit. It is also known as return inwards.
Accounting for Sales Return
Whenever there is a sale return, the seller will debit the sales return account and credit the debtor’s account. The total amount of sales returns is deducted from the gross sales for the period giving the figure for net sales. Debtor’s account is credited because the amount receivable from debtors will reduce.
The sales return is a contra account to the sales.
Format of sales return book:
In the above format, a credit note is a statement prepared by the seller and sent to the buyer. In this statement, all the details are mentioned in respect of the goods sent by the buyer and are an indication that the buyer’s account is credited in respect of the goods received.
For example, Mr. A sold goods to Mr. B costing Rs 50,000 on 1 December. On 5 December, goods amounting to Rs 15,000 were found defective and were returned immediately to Mr. A.
Mr. A will account for this in the following way:
See less