As per Wiki, it is also called construction in progress. Capital work in progress is a non-current asset of an entity. It is also known as CWIP in short. CWIP is the work which is not yet completed but the amount for which has already been paid. Suppose, at the time of preparing a balance sheet, ifRead more
As per Wiki, it is also called construction in progress. Capital work in progress is a non-current asset of an entity. It is also known as CWIP in short.
CWIP is the work which is not yet completed but the amount for which has already been paid.
Suppose, at the time of preparing a balance sheet, if an asset is not completed, all the costs incurred on that asset up to the balance sheet date are to be transferred to an account called capital work in progress.
Example 1: A machinery under installation.
There are several expenses incurred while installing machinery, expenses such as labor charges, Initial delivery and handling costs, Assembly and installation cost, etc are included in CWIP and when the asset is completed and is ready to use, all the costs are transferred to the relevant accounts.
To make it simpler, let me show journal entries relating to this example.
When an expense is incurred/paid:

When an asset is complete and put to use:

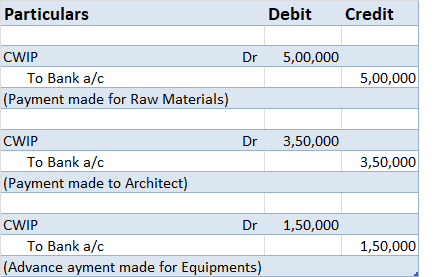
Example 2: A Contractor is constructing a building. The following expenditures are being incurred to date:
i) Raw materials – 5,00,000
ii) Payment to Architect – 3,50,000
iii) Advance for Equipments – 1,50,000
Following accounting entries will be passed to record the expenditure on CWIP assets:
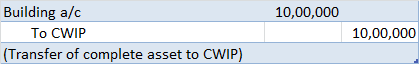
The following accounting entry will be passed once assets are ready to use:
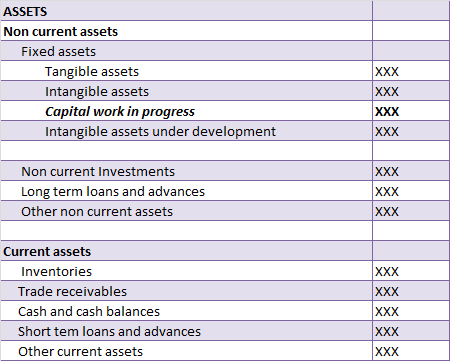
Disclosure in the Balance sheet
CWIP account is shown separately in the balance sheet below the fixed asset.
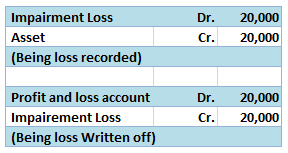
we cannot depreciate capital work in progress. It can only be depreciated when the asset is put to use.

Definition Gross profit is the excess of the proceeds of goods and services rendered during a period over their cost, before taking into account administration, selling, distribution, and financial expenses. When the result of this computation is negative it is referred to as gross loss Formula : ToRead more
Definition
Gross profit is the excess of the proceeds of goods and services rendered during a period over their cost, before taking into account administration, selling, distribution, and financial expenses.
When the result of this computation is negative it is referred to as gross loss
Formula :
Total Revenues – Cost Of Goods Sold
Net profit is defined as the excess of revenues over expenses during a particular period.
When the result of this computation is negative it is called a net loss.
Net profit may be shown before or after tax.
Formula :
Total Revenues – Expenses
Or
Total Revenues – Total Cost ( Implicit And Explicit Cost )
The basic difference between gross profit and net profit is that gross profit estimates the profitability of a company whereas net profit is to show the performance of the company.
Key points of Gross Profit
Some of the key points of as for gross profits follows :
• Stage of calculation: Gross Profit is calculated in the first stage of the Final Account.
• Purpose of calculation: It is calculated to know the total profit earned during the particular accounting
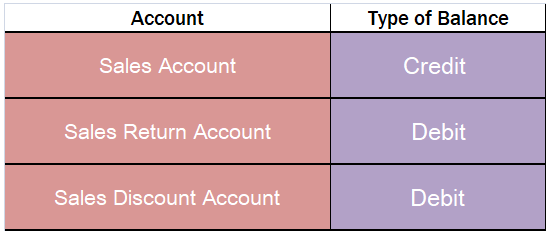
• Type of balance: Gross Profit shows the credit balance of the Trading Account.
• Dimension: It is a narrow concept as it is a part of Net Profit.
• Treatment: It is not treated directly in the balance sheet. It is transferred to the Profit And Loss Account.
Key points of Net Profit
Some of the key points of as for gross profits follows :
• Stage of calculation: Net Profit is calculated in the second stage of the Final Account.
• Purpose of calculation: It is calculated to know the net profit earned during the particular accounting
• Type of balance: Net Profit shows the credit balance of the Profit And Loss Account.
• Dimension: It is a wider concept as it includes Gross Profit.
• Treatment: It is treated directly in the balance sheet by adding or subtracting from the capital.
Examples
Now let me explain to you by taking an example which is as follows :
In a business organization there were the following data given as purchases made Rs 73000, inventory, in the beginning, was Rs 10000, direct expenses made were Rs 7000, closing inventory which was Rs 5000, revenue from operation during the period was Rs 100000.
Then,
COST OF GOODS SOLD = Purchases + Opening Inventory + Direct Expenses – Closing Inventory.
= Rs ( 73000 + 10000+ 7000- 5000)
= Rs 85000
GROSS PROFIT = REVENUE – COST OF GOODS SOLD
= Rs ( 100000 – 85000 )
= Rs 15000
Now from the above question keeping the gross profit same if the indirect expenses of the organization are Rs 2000 and the other income is Rs 1000.
Then,
NET PROFIT = GROSS PROFIT – INDIRECT EXPENSES + OTHER INCOMES
= Rs ( 15000 – 2000 + 1000)
= Rs 14000
Conclusion
So here I conclude that gross profit is the difference between revenues from sales and/or services rendered and its direct cost.
Whereas net profit is after the deduction of total expenses from the total revenues of the enterprise.
See less