To ascertain the debtors and creditors of the business To ascertain the financial position of the business To ascertain the profit or loss of the business To ascertain the collective effect of all ...
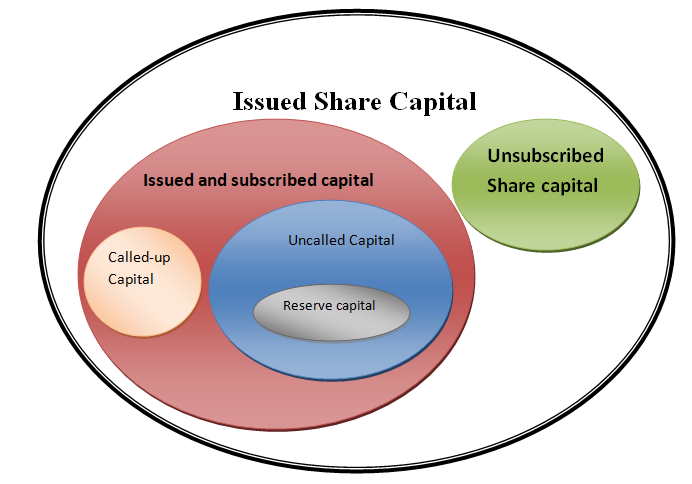
Reserve capital is part of ‘Uncalled capital’. ‘Uncalled capital’ means the outstanding amount on shares on which the call money is not yet called. A company may issue its shares and receive the money either in full or in instalments. The instalments are named: Application money – Received by a compRead more
Reserve capital is part of ‘Uncalled capital’. ‘Uncalled capital’ means the outstanding amount on shares on which the call money is not yet called.
A company may issue its shares and receive the money either in full or in instalments. The instalments are named:
- Application money – Received by a company from the people who apply for allotment of the shares.
- Allotment money – Called by the company from the people to whom the shares are allotted at the time of allotment.
- Call money – The outstanding amount is called by way of call money in one or more instalments.
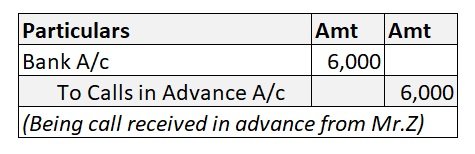
For example, X Ltd issues 1000 shares at a price of Rs. 100 per share which is payable Rs. 25 at application, Rs. 30 at the allotment, Rs. 25 at the first call and Rs. 20 at the second and final call.
The shares at fully subscribed and X Ltd has called and received money till the first call. The second call is not made yet.
This amount of Rs 20,000 (1000 x Rs.20) will be uncalled capital.
Now, It is up to the management when to make the second and final call.
If the management shows no intention of calling the outstanding money on such shares, then the uncalled capital will be called reserve capital.
Such shares which are not fully called are known as party paid shares.
It is ultimately payable to the company by the shareholders of partly paid shares at the time of dissolution.
Reserve capital is not shown either in the balance sheet or in the notes to accounts to the balance sheet. But one can ascertain it just by examining the notes to accounts to the balance. If the shares are partly paid and the management seems to have no intention of calling the outstanding money then such uncalled share capital is reserve capital.
Reserve capital is neither a liability nor an asset for the company.
But at the time of winding up of the company, it becomes a liability for the shareholders to pay the balance amount of their shares.
By now, you must have understood why reserve capital is not part of unsubscribed capital. It is because reserve capital is related to shares that are issued and subscribed.

The correct answer is 4. To ascertain the collective effect of all transactions pertaining to a particular account. The reason being is that in the ledger account all the effects are recorded for example, how much money is spent on a particular type of expense or how much money is receivable from aRead more
The correct answer is 4. To ascertain the collective effect of all transactions pertaining to a particular account. The reason being is that in the ledger account all the effects are recorded for example, how much money is spent on a particular type of expense or how much money is receivable from a debtor. In ledger accounts, information can be obtained about a particular account.
Ledger is the Principal book of accounts and also called the book of final entry. It summarises all types of accounts whether it is an Asset A/c, Liability A/c, Income A/c, or Expense A/c. The transactions recorded in the Journal/Subsidiary books are transferred to the respective ledger accounts opened.
Importance of preparing ledger accounts:
- Ledger accounts get the ready results i.e. helps in identifying the amount payable or receivable.
- It is necessary for the preparation of the Trial Balance.
- The financial position of the business is easily available with the help of Assets A/c and Liabilities A/c.
- It helps in preparing various types of income statements on the basis of balances shown in ledger accounts.
- It can be used as a control tool as it shows balances of various accounts.
- It is useful for the management to forecast or plan for the future.
See less