Fluctuating Capital Fluctuating capital is a capital that is unstable and keeps changing frequently. In the fluctuating capital, the capital of each partner changes from time to time. In partnership firms, each partner will have a separate capital account. Any additional capital introduced during thRead more
Fluctuating Capital
Fluctuating capital is a capital that is unstable and keeps changing frequently. In the fluctuating capital, the capital of each partner changes from time to time. In partnership firms, each partner will have a separate capital account. Any additional capital introduced during the year will also be credited to their capital account. In the fluctuating capital method, only one capital a/c is maintained i.e no current accounts like in the fixed capital a/c method. Therefore, all the adjustments like interest on capital, drawings, etc. are completed in the capital a/c itself.
It is most commonly seen in partnership firms and it is not essential to mention the Fluctuating Account Method in the partnership deed.
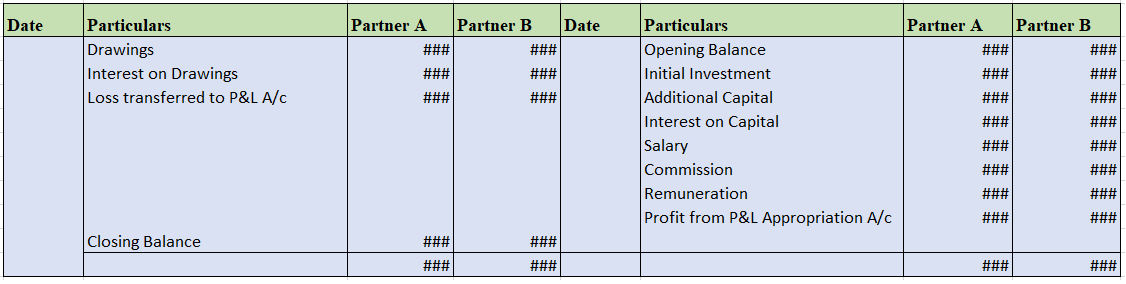
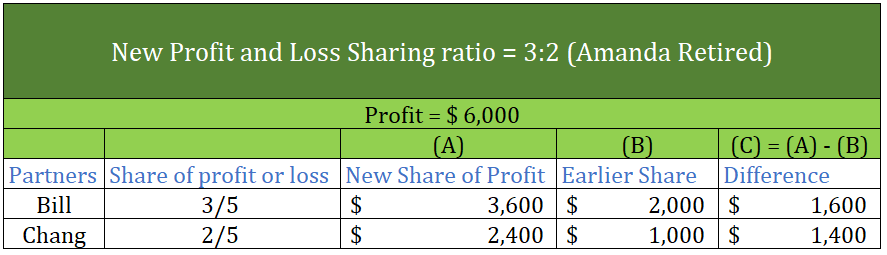
- All the adjustments resulting in a decrease in the capital will be debited to the partner’s capital, such as drawings made by each partner, interest on drawings, and share of loss.
- Similarly, the activities or adjustments that lead to an increase in the capital are credited to the partner’s capital account, such as interest on capital, salary, the share of profit, and so on.
Fluctuating Capital Account Format
See less

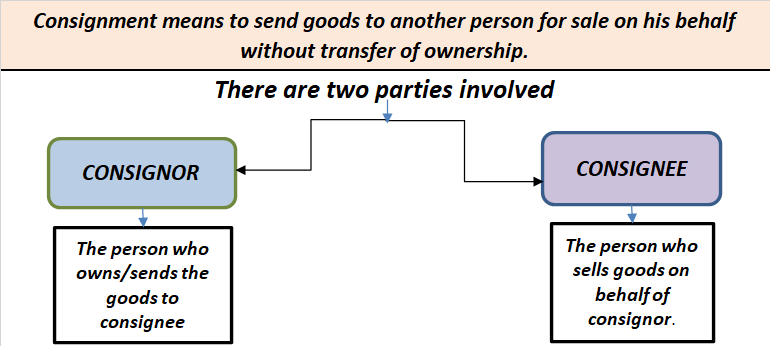
Income and Expenditure A/c of Charitable Trust Income and Expenditure A/c is like the Profit and Loss A/c in the Balance Sheet of the Charitable Trust. All the income and expenses are, therefore, recorded in this. It is used to determine the surplus or deficit of income over expenditures over a specRead more
Income and Expenditure A/c of Charitable Trust
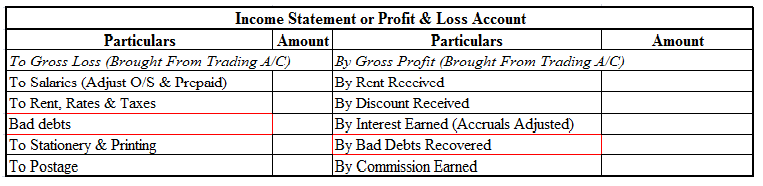
Income and Expenditure A/c is like the Profit and Loss A/c in the Balance Sheet of the Charitable Trust. All the income and expenses are, therefore, recorded in this. It is used to determine the surplus or deficit of income over expenditures over a specific accounting period.
It shows the summary of all the income and expenditures done by the charitable trust over an accounting year. All the revenue items relating to the current period are shown in this account, the expenses and losses on the expenditure side, and incomes and gains on the income side of the account.
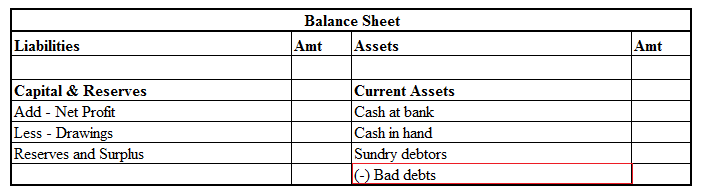
Later on, they are even used in the Balance Sheet. As follows-
On the Assets Side
On the Liability Side
See less