Before we jump in the concept of valuation of Goodwill, let us first understand the meaning of term “Goodwill”. Goodwill is an Intangible asset of the business. As the definition of Intangible asset, Goodwill cannot be seen or felt. In simple words it is business’s worth or its reputation earned oveRead more
Before we jump in the concept of valuation of Goodwill, let us first understand the meaning of term “Goodwill”.
Goodwill is an Intangible asset of the business. As the definition of Intangible asset, Goodwill cannot be seen or felt. In simple words it is business’s worth or its reputation earned over a period of time.
Calculation of value of the goodwill in monetary terms is done at the time of merger or acquisition of the business. Goodwill is often applied to businesses which are earning large number of profits, have crucial corporate links and large customer/client base.
Self-earned goodwill is never shown in monetary terms in business’s own balance sheet while goodwill which is purchased is shown in the asset side of the balance sheet of the buyer business.
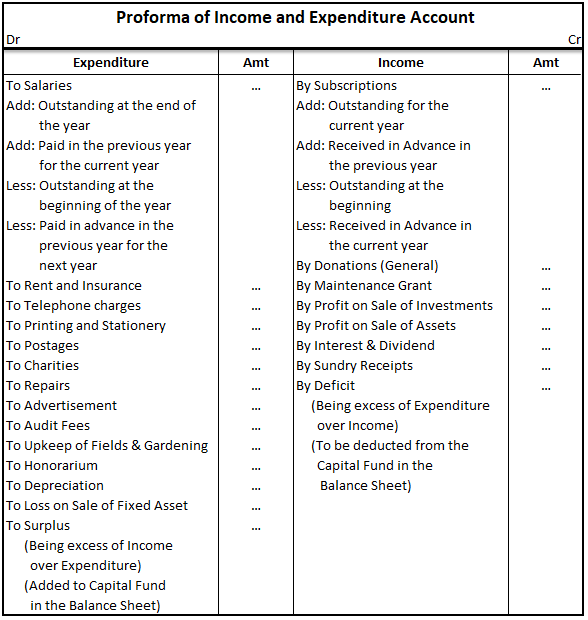
Following are the methods under which goodwill can be valued:
- Average Profit Method – In this method, Goodwill is calculated by average profits multiplied by the number of years purchased. Typically, last 5-6 years profit figures are taken ignoring any abnormal gains or loss during the year. Formula for the same would be as follows:
Goodwill = Average Profit x No. of Years Purchase
- Weighted Average Method – This method is updated method of average profit method, Profits of the previous years are calculated by specific number of weights. This method is useful when there is a lot of fluctuations in the profits and importance has to be given to current year’s profit. Formula for the same would be as follows:
Goodwill = Weighted Average Profit x No. of Years Purchase
Where,
Weighted Average Profit = Sum of Profits multiplied by weights / Sum of Weights
- Super Profit Method – Super profit is additional profit generated by the business over normal profit. Further for the calculation, Super profit is capitalized by the normal rate of return and resulting figure is value of Goodwill.
Formula for the same would be as follows:
Goodwill = Super Profits x (100/Normal Rate of Return)
- Annuity Method – In this method, Discounted amount of the super profits is calculated by taking into consideration the current value of the annuity at rate of return.
Formula for the same would be as follows:
Goodwill = Super Profit x Discounting Factor
- Capitalization Method – In this method, existing capital employed is deducted from capitalized number of average profits or super profits. The resulting figure is Goodwill.
Formula for the same would be as follows:
a. Average Profit Capitalization Method –
Goodwill = [Average Profit / Normal Rate of Return x 100] – Capital Employed
b. Super Profit Capitalization Method –
Goodwill = Super Profits x (100/ Normal Rate of Return)
See less

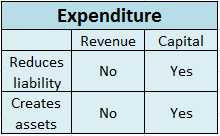
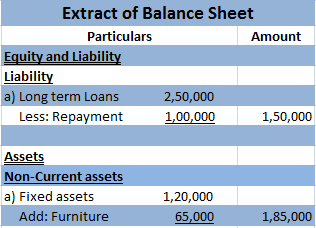
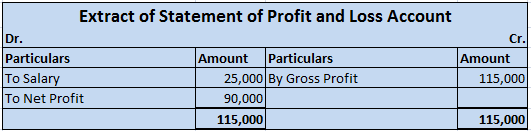
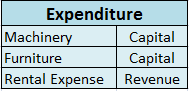
An asset is a resource in the name of the company or controlled by the company that holds economic value and will provide it future benefits. A company invests in various kinds of assets for manufacturing purposes and investment purposes as well. Some examples of assets are: Plant and Machinery InveRead more
An asset is a resource in the name of the company or controlled by the company that holds economic value and will provide it future benefits.
A company invests in various kinds of assets for manufacturing purposes and investment purposes as well. Some examples of assets are:
Assets can be broadly divided into two categories based on their physical existence:
Tangible Assets can be further divided into two categories based on their life and role in the operating cycle:
Since the company derives benefit from the asset, an asset account is debit in nature. If an asset account has a credit balance, it would fundamentally make it a liability. However, there are certain exceptions to it.
In the case of Bank Overdraft, which means a company withdraws more from the bank than it has deposited in its account, Bank Account can also be shown having a credit balance.
Contra Assets Accounts are the accounts that are contrary to the basic nature of an assets account, that is it is contrary to the debit nature of the assets account and hence are credit in nature.
Examples of Contra Assets Account are:
Accumulated Depreciation Account which is essentially Plant Assets Account also has a credit balance as it is used to depreciate the asset, or in other words, reduce the value of the assets, hence it also has a credit balance.
When there are balances in the Account Receivables Account that are not paid to the company or have a very low probability of being paid, they are recorded in a separate account called Bad Debts Account, which is also credit in nature.
See less