Meaning The term ‘Sundry creditors’ consist of two words: ‘Sundry’ and ‘creditors’. The word ‘sundry’ means the items which are not significant enough to be named separately. It also refers to a collection of miscellaneous items. Creditors are the person from whom money is borrowed or goods are puRead more
Meaning
The term ‘Sundry creditors’ consist of two words: ‘Sundry’ and ‘creditors’.
The word ‘sundry’ means the items which are not significant enough to be named separately. It also refers to a collection of miscellaneous items.
Creditors are the person from whom money is borrowed or goods are purchased on credit by a business or a non-business entity. They have to be repaid after a period of time which is usually less than or up to one year.
By combining the meaning of both words, ’sundry’ and ‘creditor’, the term ‘sundry creditor’ will refer to the collection of insignificant creditors of an entity.
Back in the days when accounting records were maintained on paper, only the records of those creditors were maintained separately, from whom goods are purchased regularly and in large amounts.
But there used to be numerous other creditors with whom the transactions were occasional and insignificant. To reduce the paperwork, records of all such creditors were maintained on a single page or book under the head ‘Sundry Creditors’
Nowadays, as accounting records are maintained digitally, hence maintaining records of each and every creditor is not a problem.
Hence, every creditor whether small or big, is grouped under the head ‘Sundry creditor’ or ‘Trade Creditor’.
Accounting Treatment
Sundry creditors are the persons to whom a business owes money.
Hence, as per golden rules of accounting, Sundry creditor is a personal account and the golden rule for personal account is, ‘Debit the receiver and credit the giver’
We know sundry creditors are liabilities, hence, as per modern rule of accounting, sundry creditors are credited in case of increase and debited in case of decrease.
Example, a business purchased goods for Rs. 10,000 from ABC & Co. The journal entry will as follows:

Here, ABC & Co is the creditor. It is credited as it is a personal account and the creditor has given the goods to the business, hence the giver is credited.
From point of view of modern rules of accounting, ABC & Co. is a creditor, a liability. On purchase of goods on credit, a liability is created. Hence, ABC & Co A/c is credited.
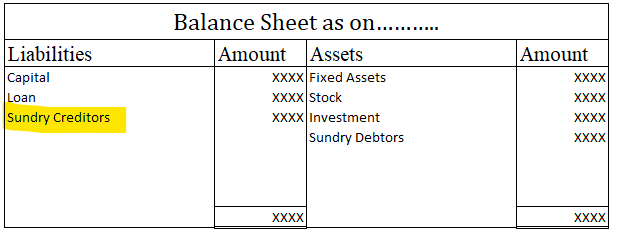
Balance sheet
Sundry creditor is a current liability, so it is shown on the liabilities side of a balance sheet. Trade payable and accounts payable mean sundry creditors only.

You must have knowledge of what depreciation is. Depreciation is the process of allocating the value of an asset over its useful life. It reduces the carrying value of the asset year by year till it is scraped. It is an expense (expense of using the asset for business purposes) and it is charged toRead more
You must have knowledge of what depreciation is. Depreciation is the process of allocating the value of an asset over its useful life. It reduces the carrying value of the asset year by year till it is scraped.
It is an expense (expense of using the asset for business purposes) and it is charged to profit and loss account.
Depreciation can be reported in the financial statement in two ways:
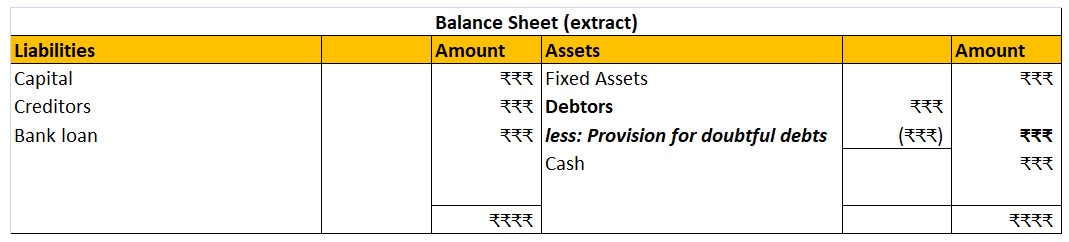
Provision for depreciation account represents the collection of total depreciation till date on an asset. That’s why it is also called accumulated depreciation account. When an asset is sold, its accumulated depreciation is credited to the asset account. See the journal entry below:
It is shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet. It is a nominal account because it is shown as an expense in the statement of profit or loss.
In case provision for depreciation account is not maintained then the balance sheet looks like this:

See less