Interest on capital is the interest provided on the capital invested in the business. It is calculated as a percentage on the capital invested. Interest on capital is provided if there is any rule established by the owner of the capital. Otherwise, it is not provided. We generally encounter ‘InteresRead more
Interest on capital is the interest provided on the capital invested in the business. It is calculated as a percentage on the capital invested. Interest on capital is provided if there is any rule established by the owner of the capital. Otherwise, it is not provided.
We generally encounter ‘Interest on capital’ in partnership accounting but a sole proprietorship can also provide interest on capital.
Interest on capital is charged or appropriated from the profits of the firm. Hence, it appears on the debit side of the profit and loss account.
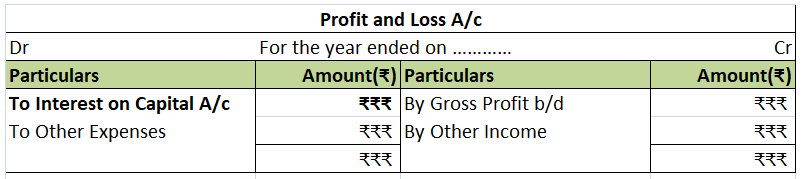
The journal entry is as follows:
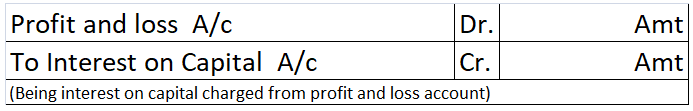
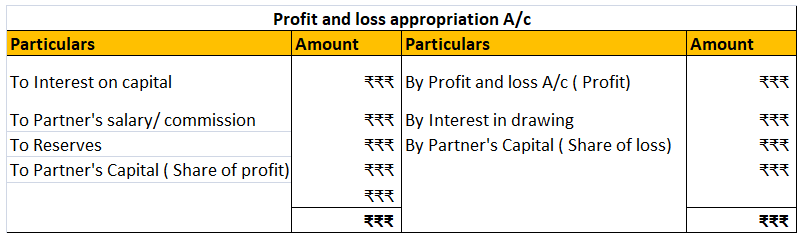
The partners, in case the firm makes profit, are provided interest on their capital balance apart from their share of profit if provision of interest on capital is mentioned in the partnership deed.
Hence, interest on capital is an appropriation of profit in partnership accounting. The journal in case of partnership account is as follows:
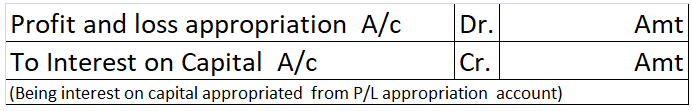
The Interest on capital is credited to the capital/ partners’ capital account thereby increasing the capital balance. The journal is as follows:

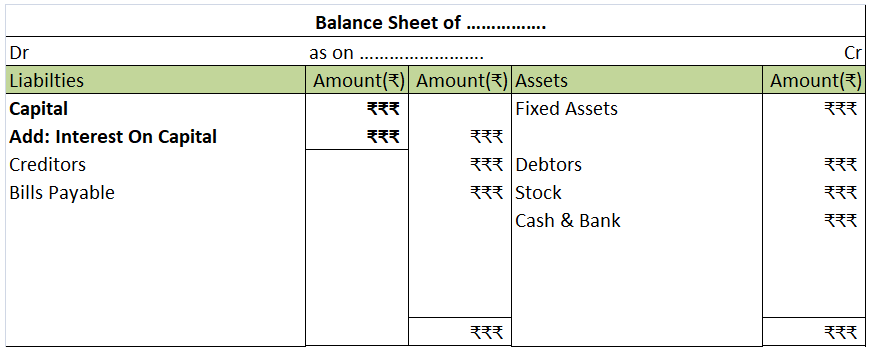
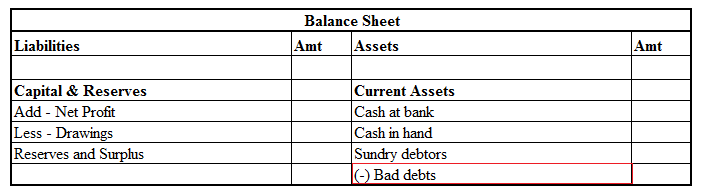
In the balance sheet it is shown as an addition to the capital account.
Numerical example
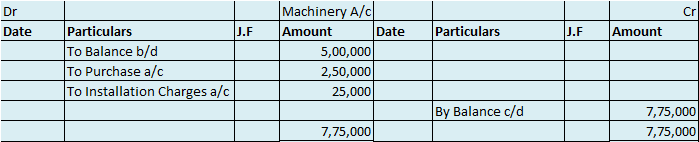
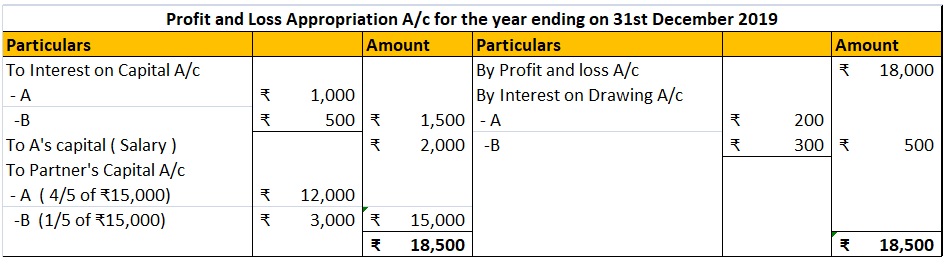
P, Q and R are partners. Their firm reported a net profit of ₹ 20,000. Their capitals are ₹30,000, ₹45,000 and ₹60,000. It is in their partnership deed to provide the partners 4% interest on capital and a salary of ₹5,000 per annum for Q. Calculate the interest on capital.
Solution:
Interest on capital to be provided to the partners:
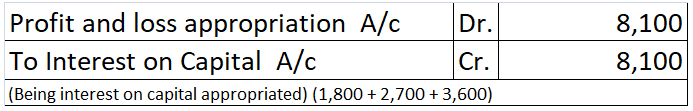
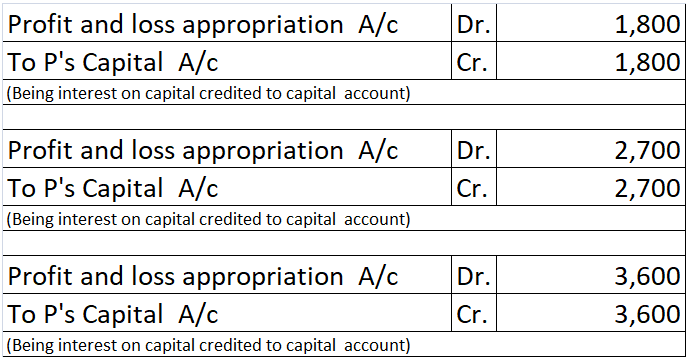
P – ₹30,000 x 6% = ₹1,800
Q – ₹45,000 x 6% = ₹2,700
R – ₹60,000 x 6% = ₹3,600
This interest will be credited to the partners’ capital. The journals are as follows:


Retained Earnings refer to the total net profits left with the company after deduction of all dividends. This amount is a source of internal finance and can be used for the growth or expansion of the company. Retained earnings are shown under shareholders’ equity in the balance sheet and are calculaRead more
Retained Earnings refer to the total net profits left with the company after deduction of all dividends. This amount is a source of internal finance and can be used for the growth or expansion of the company.
Retained earnings are shown under shareholders’ equity in the balance sheet and are calculated as follows:
Retained earnings at the end of the year = Retained earnings at the beginning of the year + Net Income – Dividend
From the above formula, Yes, it is possible for retained earnings to be negative. Negative earnings occur when the cumulative dividend payout is higher than the earnings made by a company during the year. This results in a negative balance as per the formula.
Negative Retained earnings indicate a number of concerning facts about a company:
Positive Retained Earnings
When a company is said to have positive retained earnings, the company has several advantages. The company has excess profit to hold on to. This helps in expansion and also acts as a safety net in case of unforeseen expenses. Hence if a company shows positive Retained earnings it can be interpreted that the company is profitable.
However, higher retained earnings mean the distribution of lesser dividends to shareholders. This makes the company look less attractive to investors. Another reason for high retained earnings could be that the company has not found any profitable investment for its earnings.
Therefore, there should be adequate retained earnings with the company but at the same time, keep a check that the amount of retained earnings does not exceed a limit.
See less