Meaning of Workmen's Compensation Reserve Workmen compensation reserve is a reserve created to compensate the labourers and employees of a firm in case of an uncertain future event in the line with their work. For example, if a labourer or group of labourers get injured seriously while working on thRead more
Meaning of Workmen’s Compensation Reserve
Workmen compensation reserve is a reserve created to compensate the labourers and employees of a firm in case of an uncertain future event in the line with their work. For example, if a labourer or group of labourers get injured seriously while working on the premises of the firm, then they will be compensated from the money kept aside in the workmen’s compensation reserve.
Workmen’s compensation reserve is created using the profits of a business. The journal entry for the creation of workmen compensation reserve is as follows:
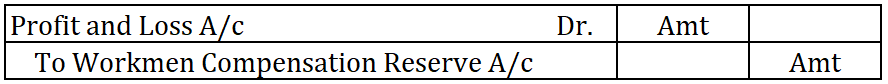
When a claim arises, the claim amount is transferred to Provision for workmen compensation claim A/c
Treatment of workmen compensation reserve in revaluation account
At the time of admission, retirement or death of partner or change in profit sharing ratio, the reserve is distributed among the old or existing partners or kept intact.
Workmen’s compensation reserve is also distributed among the old or existing partners subject to the claim arising on the reserve.
Here are the three situations:
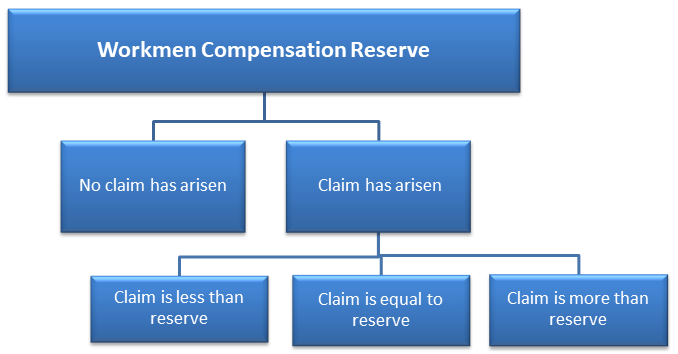
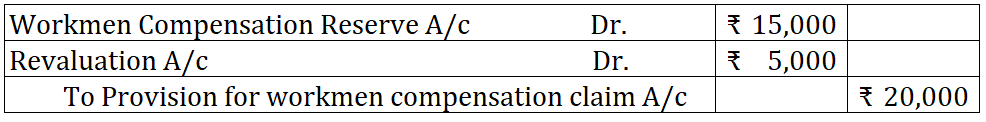
The revaluation account comes into the picture only when the claim is more than the amount available in the reserve. For example, the claim is Rs. 20,000 but the amount in the reserve is only Rs. 15,000.
In such a case, the excess claim will be met by debiting the revaluation account.
The journal will as given below:
Since the revaluation account is debited, it is a loss and this loss will be written from old or existing partners’ capital in the old profit sharing ratio. The journal entry is given below:


Fluctuating Capital Fluctuating capital is a capital that is unstable and keeps changing frequently. In the fluctuating capital, the capital of each partner changes from time to time. In partnership firms, each partner will have a separate capital account. Any additional capital introduced during thRead more
Fluctuating Capital
Fluctuating capital is a capital that is unstable and keeps changing frequently. In the fluctuating capital, the capital of each partner changes from time to time. In partnership firms, each partner will have a separate capital account. Any additional capital introduced during the year will also be credited to their capital account. In the fluctuating capital method, only one capital a/c is maintained i.e no current accounts like in the fixed capital a/c method. Therefore, all the adjustments like interest on capital, drawings, etc. are completed in the capital a/c itself.
It is most commonly seen in partnership firms and it is not essential to mention the Fluctuating Account Method in the partnership deed.
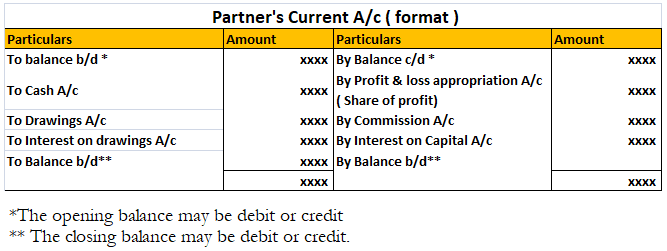
Fluctuating Capital Account Format
See less